Q1. An object is in combined rotational and translational motion. Its K.E. is
Solution
An object in combined rotational and translation motion will have K.E as the sum of kinetic energy in translation motion and in rotational motion. Forming the following equation
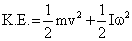
Q2. The moment of inertia of two spheres of equal masses is equal. If one of the spheres is solid of radius  m and the other is a hollow sphere. What is the radius of the hollow sphere?
m and the other is a hollow sphere. What is the radius of the hollow sphere?
 m and the other is a hollow sphere. What is the radius of the hollow sphere?
m and the other is a hollow sphere. What is the radius of the hollow sphere?Solution
Moment of inertia of solid sphere = Moment of inertia of hollow sphere
i.e.
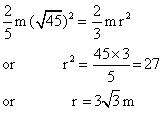
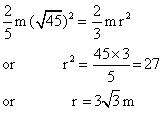
Q3. The motion of centre of mass of a system of two particles is unaffected by their internal forces
Solution
Because the centre of mass is affected only by external forces not by internal forces.
Q4. The instantaneous angular position of a point on a rotating wheel is given by the equation
 The torque on the wheel becomes zero at:
The torque on the wheel becomes zero at:
 The torque on the wheel becomes zero at:
The torque on the wheel becomes zero at:Solution


Q5. There are two objects of masses 1 kg and 2 kg located at (1, 2) and (-1, 3) respectively. The coordinates of the centre of mass are
Solution


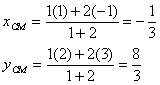
Q6. The angular momentum of a system of particles is not conserved when
Solution
Angular momentum can change only when external torque acts on the system
Q7. Arrange the comparative stabilities of the three objects shown in the figure in terms of work and potential energy.
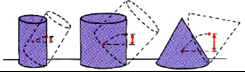

Solution
When each one is tipped, its centre of mass is raised. This means each one is now sitting in stable equilibrium. Going from left to right, as each one is tipped, its centre of mass or centre of gravity is raised more than the one to its left. That means more work is done to tip each succeeding one. That means each one is more stable than the one on its left.
Q8. The centre of gravity of three truks parked on a hill are shown.Which of the following trucks will topple over? 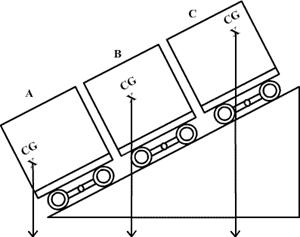

Solution
The line dropped from the center of gravity passes through area of the truck's base of support in the case of trucks B and C. While, in case of truck A, the line from centre of gravity fall outside its base of support. Hence, truck A topples over, but trucks B and C are stable.
Q9. In case of a projectile, the angular momentum is minimum
Solution
Q10. Two discs of moments of inertia I1 and I2 about their respective axes (normal to the disc and passing through the centre), and rotating with angular speeds I1 and I2 are brought into contact face to face with their axes of rotation coincident. What is the angular speed of the two disc system?
Solution

Q11. A solid cylinder rolls down an inclined plane of height 6m and reaches the bottom of the plane with angular velocity of 2 rad/s. The radius of the cylinder must be
Solution

Q12. A body is moving with constant velocity parallel to x axis. Its angular momentum w.r.t origin will
Solution
Angular momentum L = r × p
L = mv (rsinθ)
Neither p (mv) nor perpendicular distance from x axis(r sinθ) changes hence angular momentum(L) with respect to origin remains constant.
Q13. The centre of mass of a system of particles does not depend on
Solution
The centre of mass of a system of particles does not depend on forces on the particles.
Q14. Two rings have their moment of inertia in the ratio 2:1 and their diameters are in the ratio 2:1. The ratio of their masses will be:
Solution
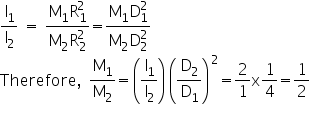
Q15. When external forces acting on a body are zero, then its centre of mass
Solution
When external forces acting on a body are zero, then its centre of mass either remains stationary or moves with uniform velocity.
Q16. Which of the following options are correct,
where i, j and k are unit vectors along the x, y and z axis?
Solution
When two vectors are perpendicular to each other, then dot product is zero and cross product gives the third vector in perpendicular direction.
Hence, dot product between i, j and k vectors will be zero and cross product will yield the third vector. Also cross product is cyclic, i.e.,


Q17. In the absence of an external torque on a system, which of the following will not change?
Solution
Q18. An external torque will always cause a change in
Solution
According to the principle of angular momentum:
When no external torque acts on a system of particles, then the total angular momentum of the system always remains constant.
Q19. Find the coefficient of friction of a solid cylinder which rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with  .
.
Solution
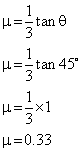
Q20. The rotational analog to the expression F = ma in linear motion is ___________in rotational motion.
Solution
Torque is analogous to force, moment of inertia to mass and angular acceleration to linear acceleration.
Q21. Relation between torque and angular momentum is similar to the relation between
Solution
Q22. Centre of gravity is the point where
Solution
Centre of gravity is the point where the entire weight of the object acts and the total gravitational torque on the body is zero.
Q23. On a toy comprising of a disc of radius 4 m, a bird is sitting on the periphery (the outer edge). Find the instantaneous velocity of the bird if disk is rotating at 180 revolutions per minute.
Solution
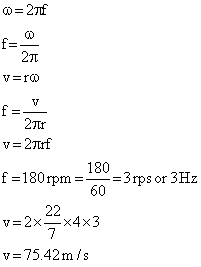
Q24. Two blocks of the masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of negligible mass and placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. An impulse gives a velocity of 14 m/s to the heavier block. The velocity of centre of mass is
Solution
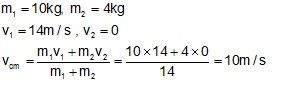
Q25. As a dancer performs a pirouette on her toes and draws her hands closer and starts spinning faster. This can be explained using
Solution
Conservation of angular momentum explains this. When she folds her arms and draws her hands closer her moment of inertia decreases and so as to keep angular momentum constant, angular velocity increases.
Q26. Why do we prefer to use a wrench with a long arm?
Solution
Torque or turning effect due to a force is maximum when r is maximum.We prefer to use a wrench with long arm because when the length of the arm(r) is long, the force (F) required to produce a given turning effect (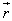 x
x 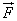 ) is smaller. Hence, a nut can be unscrewed easily.
) is smaller. Hence, a nut can be unscrewed easily.
Q27. Which of the following is an axial vector?
Solution
Torque is an axial vector.Axial vectors are those vectors which represent rotational effect and act along the axis of rotation. Eg: Angular velocity, torque, angular momentum etc are axial vectors.
Q28. The figure shows a dish kept at an orientation with a marble placed on it. If the marble in figure is displaced slightly, it would rattle about for a while and come to rest in its original place. This is an example of :
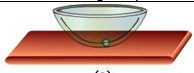

Solution
If a dish is kept at an orientation with a marble placed on it and if the marble in figure is displaced slightly, it would rattle about for a while and come to rest in its original place. This is the example of Stable Equilibrium.
When a body tries to regain its equilibrium position after being slightly displaced and released, it is said to be in stable equilibrium.
Q29. To maximize torque on a lever, which of the following will not help?
Solution
To maximize torque, you need to:
i. Increase the magnitude of the force
ii. Increase the distance, r, from the axis of rotation of the point where we apply the force.
iii. Apply the force in a direction perpendicular to the lever.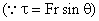
Q30. A circus acrobat while performing spins brings his limbs closer to the body. Due to this
Solution
A circus acrobat while performing spins brings his limbs closer to the body. Due to this Angular Momentum is conserved but K.E. is not conserved. Because when the moment of inertia decreases, rotational kinetic energy increases as work is done in decreasing the moment of inertia of the body.
Q31. Two identical particles move towards each other with velocity 2v and v respectively. The velocity of the centre of mass is
Solution
Q32. The length of the second hand of a clock is 7 cm. Find the speed of the tip of the hand.
Solution
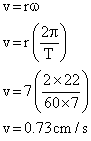
Q33. Let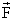 be force acting on a particle having position vector
be force acting on a particle having position vector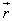 . Let
. Let 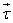 be the Torque of this force about the origin. Then
be the Torque of this force about the origin. Then
Solution

Q34. A rotor of mass 500 kg makes 210 revolutions per minute. To maintain its uniform angular speed ω, an engine needs to transmit a torque of 180 N m. What is the power of the engine required?
Solution
Given:
m= 500kg
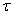 = 180Nm
n = 2100 rpm = 2100/60 rps
= 180Nm
n = 2100 rpm = 2100/60 rps
 = 2 x (3.14) x (2100/60)
= 220 rad/s
As P =
= 2 x (3.14) x (2100/60)
= 220 rad/s
As P = 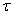 ω
= 180 x 220
= 39600 watt= 39.6 kW.
ω
= 180 x 220
= 39600 watt= 39.6 kW.
 = 2 x (3.14) x (2100/60)
= 220 rad/s
As P =
= 2 x (3.14) x (2100/60)
= 220 rad/s
As P =
Q35. A stick is thrown in the air and lands on the ground at same distance from the thrower. The centre of mass of the stick will move along a parabolic path
Solution
In all the cases given the centre of mass of the stick will move along a parabolic path.
Q36. The SI unit of moment of inertia is:
Solution
The SI unit of moment of inertia is kgm2
Q37. A sphere of mass 1 kg and radius 1m rotates with a speed of 100 rpm about the axis passing through its centre. Calculate the angular momentum.
Solution
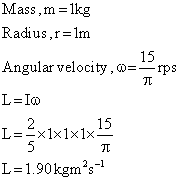
Q38. The centre of mass is a point
Solution
The centre of mass is a point where the whole mass is supposed to be concentrated.
Q39. Angular momentum of a body is the product of
Solution
Angular momentum of a body about a given axis is the product of linear momentum (p) of a particle and the perpendicular distance of the line of action of linear momentum vector from axis of rotation.
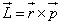
Q40. There are two circular iron discs A and B having masses in the ratio 1:2 and diameter in the ratio 2:1. The ratio of their moment of inertia is
Solution
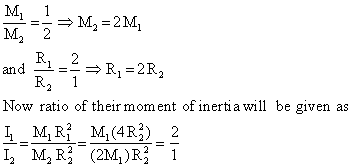
Q41. What is the physical meaning of angular momentum?
Solution
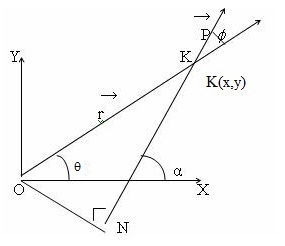 If K(x,y) is the position of a particle of mass m and linear momentum
If K(x,y) is the position of a particle of mass m and linear momentum  rotating X-Y plane .
rotating X-Y plane .
 L = pr
L = pr
Q42. kg m2 s-1 is the unit of
Solution
kg m2 s-1 is the unit of angular momentum.
Q43. All the points of a rigid body rotating about the given axis have same :
Solution
All the points of a rigid body rotating about the given axis have same angular velocity.
Q44. A rotating machine is maintained at a uniform angular speed of 150 rad s-1, with a torque of 100 Nm. The power is
Solution

Q45. What is the relation between torque and angular momentum?
Solution
Torque is also defined as the rate of change of angular momentum.i.e.
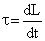
Q46. Explain the motion of Earth-Moon system around the sun in terms of centre of mass concept.
Solution
The moon revolves around the earth in a circular orbit and the earth goes around the sun in an elliptical orbit. Actually, the Earth-Moon system revolves about their common centre of mass in elliptical path.
As the mass of earth is very large as compared to that of the moon, the centre of mass of the Earth-Moon system lies within the earth and it appears that the moon revolves around the earth but the reality is that both revolve around their common centre of mass.
Q47. For a rotating wheel of 4m radius and linear velocity of 10m/s find the centripetal acceleration.
Solution
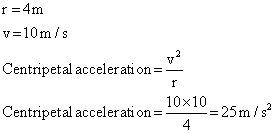
Q48. A merry- go- round ( diameter 4.0 m ) starts from rest and uniformly accelerates until it rotates at 0.8 rev/min. This occurs in 11s. Once it has reached this rate , it rotates at 0.8 rev/min uniformly . Determine the angular acceleration
Solution

Q49. A ring has greater moment of inertia than a circular disc of same mass and radius, about an axis passing through its centre of mass perpendicular to its plane, because
Solution
A ring has a larger moment of inertia because its entire mass is concentrated at the rim at maximum distance from the axis.
Q50. Why the door cannot be rotated by applying force in a direction parallel to the plank of the door?
Solution
We know that
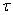 = r Fsin Φ ----------------------------------------(1)
When, force is applied in a direction parallel to
= r Fsin Φ ----------------------------------------(1)
When, force is applied in a direction parallel to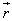 .
Φ = 0° or 180°
Therefore sin Φ=0
Substituting in eq(1), we get
Torque (
.
Φ = 0° or 180°
Therefore sin Φ=0
Substituting in eq(1), we get
Torque (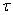 ) = 0
Therefore, Torque of the force is zero. So, the door cannot be rotated by applying force in a direction parallel to the plank of the door.
) = 0
Therefore, Torque of the force is zero. So, the door cannot be rotated by applying force in a direction parallel to the plank of the door.
Q51. A circus acrobat while performing spins brings his limbs closer to the body. Due to this
Solution
A circus acrobat while performing spins brings his limbs closer to the body. Due to this moment of inertia decreases and angular velocity increases.
Q52. A particle of mass m is rotating in a plane in circle with an angular momentum L. What is the centripetal force acting on the particle?
Solution
Given, angular momentum = L
We know that L = mvr
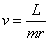 -----------------------------------------------1
The centripetal force on the particle,
F =
-----------------------------------------------1
The centripetal force on the particle,
F = 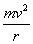 ------------------------------------------------2
Put the value of v from eq 1 in eq 2
We get,
------------------------------------------------2
Put the value of v from eq 1 in eq 2
We get,
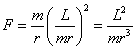
Q53. The moment of inertia of a body depends on
Solution
The moment of inertia of a body depends on Shape of body, Size of body, Distribution of mass of body about the axis of rotation, Position and Orientation of the axis of rotation.
Q54. A rigid body is one
Solution
A body that does not deform under the influence of forces and in many situations the deformations are negligible and in which the distance between all pairs of particles remains fixed is called a rigid body.
Q55. If a man of mass M jumps to the ground from height h and his centre of mass moves a distance x in the time taken by him to hit the ground, the average force acting on him is (assuming his retardation to be constant during his impact with the ground)
Solution
Since centre of mass move through distance x, the average force is given by:
Fx = Mgh
F = Mgh/x
Q56. If the resultant of all external forces is zero, then velocity of centre of mass will be
Solution
If the resultant of all external forces is zero, then velocity of centre of mass will be constant.
Q57. Using the expression for power and kinetic energy ( ) of rotational motion, derive the relation
) of rotational motion, derive the relation 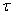 =I
=I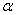 , where the symbols have their usual meaning.
, where the symbols have their usual meaning.
 ) of rotational motion, derive the relation
) of rotational motion, derive the relation Solution
Given kinetic energy of rotation
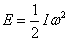 ---------------------------(1)
Where I = moment of inertia
---------------------------(1)
Where I = moment of inertia
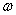 = angular velocity
We know that power associated with torque in rotational motion is given by
P=
= angular velocity
We know that power associated with torque in rotational motion is given by
P=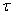 ω ---------------------------(2)
Also, power = rate of doing work in rotational motion and work is stored in the body in the form of kinetic energy.
Therefore,
P =
ω ---------------------------(2)
Also, power = rate of doing work in rotational motion and work is stored in the body in the form of kinetic energy.
Therefore,
P = 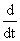 (kinetic energy of rotation)
P =
(kinetic energy of rotation)
P = 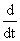 (
(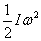 ) -------------------------- from (1)
P =
) -------------------------- from (1)
P = 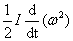 P =
P = 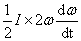 P =
P =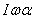 --------------------------(3) (Because
--------------------------(3) (Because 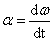 )
From eq.2 and 3
)
From eq.2 and 3
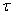 ω =
ω = 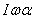 Therefore,
Therefore, 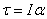
Q58. The Equations of Rotational Motion are
Solution
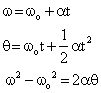 These are the three equations of rotation; they correspond to the three equations of linear motion.
These are the three equations of rotation; they correspond to the three equations of linear motion.
Q59. A wheel having moment of inertia 3.5 kgm2 rotates about the vertical axis. The torque required to produce an angular acceleration of 25rad/s2 in the wheel is
Solution
I= 3.5 kg m 2 ,α= 25 rad/s 2
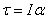 = 3.5 kg m 2 x 25 rad/s 2
= 87.5 N m.
= 3.5 kg m 2 x 25 rad/s 2
= 87.5 N m.
Q60. A cap of pen can be easily opened with the help of two fingers than one finger. Why?
Solution
The force applied using two fingers constitute a couple or torque and the cap of pen can be turned easily. But with one finger, only a single force can be applied.
Q61. The moment of inertia of a solid sphere about its diameter is 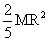 .Find moment of inertia about its tangent.
.Find moment of inertia about its tangent.
Solution
By using theorem of parallel axis,
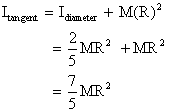 The moment of inertia of the sphere about its tangent = 7/5 M R 2
Where m is the mass and R is the radius of the sphere.
The moment of inertia of the sphere about its tangent = 7/5 M R 2
Where m is the mass and R is the radius of the sphere.
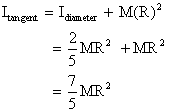 The moment of inertia of the sphere about its tangent = 7/5 M R 2
Where m is the mass and R is the radius of the sphere.
The moment of inertia of the sphere about its tangent = 7/5 M R 2
Where m is the mass and R is the radius of the sphere.
Q62. What is the rotational analogue of mass of a body?
Solution
Mass of a body is a measure of its inertia in translatory motion, and moment of inertia is the measure of rotational inertia. Therefore, moment of inertia is the rotational analogue of mass.
Q63. Two bodies A and B are attracted towards each other due to gravitation. Given that A is much heavier than B. what will you say about the relative motion of the centre of mass?
Solution
The two bodies will move towards their common centre of mass. But the location of centre of mass will remain unchanged. i.e Centre of mass remains at rest with respect to A as well as B.
Q64. The centre of mass of a body is located
Solution
The centre of mass of a body is located inside or outside the system
Q65. A car decelerates uniformly from velocity v1 to velocity v2 while getting displaced by s. If the diameter of the wheel is d, the angular acceleration of the wheel is
Solution
The acceleration 'a' of the car is given by
v22 = v12 + 2as
(we have applied th equation of linear motion, v2 = v02+2as)
Therefore, a = (v22 - v12) /2s.
The angular acceleration 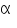 of the wheel is given by
of the wheel is given by
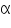 =a/r where r is the radius of the wheel (which is equal to d/2).
Therefore,
=a/r where r is the radius of the wheel (which is equal to d/2).
Therefore, 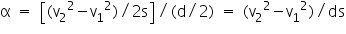
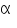 of the wheel is given by
of the wheel is given by
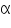 =a/r where r is the radius of the wheel (which is equal to d/2).
Therefore,
=a/r where r is the radius of the wheel (which is equal to d/2).
Therefore, 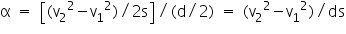
Q66. A ball is under the effect of circular motion about a perpendicular axis with respect to the reference direction. The angular position (in radians) is given by the following function 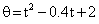 .The angular position when angular velocity is zero is
.The angular position when angular velocity is zero is
Solution
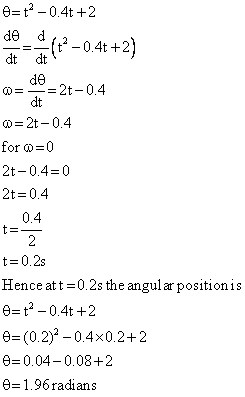
Q67. The moment of inertia of a circulating ring passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane is 400g cm2. If the radius of ring is 5 cm, find the mass of the ring.
Solution
Here, 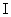 = 400 g cm2
R= 5 cm
Now, moment of inertia of the ring,
= 400 g cm2
R= 5 cm
Now, moment of inertia of the ring, 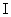 = MR2
Therefore,
= MR2
Therefore,
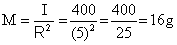
Q68. The dimensions of angular momentum are
Solution
The dimensions of angular momentum are 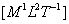 .
.
Q69. If a ball or a wheel is made to slide down an inclined plane, what kind of motion can it exhibit?
Solution
It has both translational and rotational motion simultaneously.
Q70. The moment of momentum is known as
Solution
The moment of momentum is known as angular momentum.
Q71. A body tied with string revolves uniformly in a circle. How does the angular momentum of the body change from its initial value if the string is cut suddenly?
Solution
The angular momentum of the body remains same.The body flies away tangentially, keeping angular momentum conserved as no external torque acts on the particle.
Q72. Which principle or law is responsible for high angular speed of inner layers of tornado?
Solution
The principle of angular momentum is responsible for high angular speed of inner layers of tornado.
Q73. Convex and concave lenses of same mass and radius rotate about an axis passing through their centre and perpendicular to the plane. Which one will have greater moment of inertia?
Solution
The concave lens is thin at the centre and thick at the edges. As, more mass is concentrated away from the axis of rotation in case of concave lens, it will have more moment of inertia.
Q74. The sum of moments of masses of all the particles in a system about the centre of mass is always:
Solution
The sum of moments of masses of all the particles in a system about the centre of mass is always zero.
Q75. What is the Principle of Conservation of Angular Momentum?
Solution
According to the Principle of Conservation of Angular Momentum when no external torque acts on a system of particles then the total angular momentum of the system always remain constant.


Q76. In 10 seconds the angular speed of a bike increases from 1000rpm to 1800rpm. The angular acceleration of bike is
Solution

Q77. The kinetic energy of a rolling wheel is
Solution
Rolling wheel’s K.E will comprise of both translational K.E. and Rotational K.E.
Q78. If the angular position of a body under circular motion is given by the equation:
 A torque of 7 Nm is applied on it. What is the expression for the power?
A torque of 7 Nm is applied on it. What is the expression for the power?
Solution
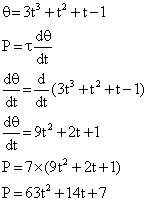
Q79. A rigid body is said to be in mechanical equilibrium if
Solution
The necessary condition for a rigid body to be in equilibrium is that:
The resultant of all the external forces must be zero.
The resultant of all the external torques must be zero.


Q80. A meter rule is supported at its centre. It is balanced by two weights, A and B. If A and B are placed at a distance 30 cm, and 60 cm from the centre of scale, find the weight of B. The weight of A is 50N.
Solution
By the principle of moment we know that, a body is balanced, when sum of clockwise moments about pivot = sum of anticlockwise moments about the same point.
Therefore,
According to principle of moment F 1 d 1=F 2 d 2
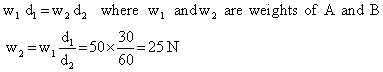
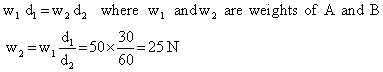
Q81. What is the purpose of attaching a flywheel on a space craft?
Solution
A flywheel is attached on a space craft for controlling the orientation of the space craft. When neither the flywheel nor the space craft is turning then the total angular momentum is zero. To change the orientation of the spacecraft, the flywheel is made to rotate. The spacecraft starts rotating in the opposite sense to maintain the angular momentum of the system zero.When the flywheel is brought to rest, the space craft also stops rotating.But the orientation of space craft changes.
Q82. If a shell at rest explodes, then, the centre of mass of the fragments
Solution
As the centre of mass is initially at rest, it will remain at rest.
Q83. Let  H and
H and 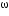 E respectively be the angular speeds of the hour hand of a watch and that of the Earth around its own axis. Compare the angular speeds of the Earth and hour hand of a watch.
E respectively be the angular speeds of the hour hand of a watch and that of the Earth around its own axis. Compare the angular speeds of the Earth and hour hand of a watch.
Solution
The time periods of hour hand and that of the Earth are 12 hours and 24 hours respectively. Now,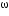 H =2 π /12 and
H =2 π /12 and
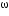 E = 2π / 24
ωE = (1/2) ωHTherefore,
E = 2π / 24
ωE = (1/2) ωHTherefore, 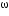 H =2
H =2  E
E
 H =2
H =2
Q84. In an equilateral triangle of length 6 cm , three masses m1= 40g , m2= 60g and m3= 60g are located at the vertices. The moment of inertia of the system about an axis along the altitude of the triangle passing through m1 is 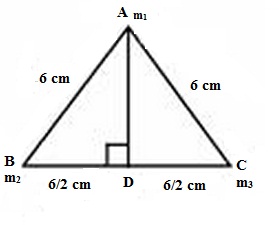

Solution
In the figure ABC is an equilateral triangle .Let AD be perpendicular to BC. i.e AD is the median of triangle ABC.
We have to find the moment of inertia of the system about AD.
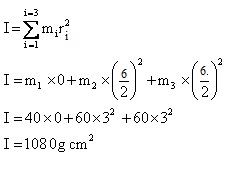
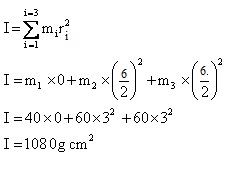
Q85. What do you mean by rolling and precessional motion of a rigid body?
Solution
Rolling Motion- Rolling motion is a combination of both translatory and rotatory motion about a fixed axis.
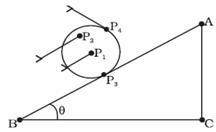 The above fig shows a rolling motion of a cylinder. Points
The above fig shows a rolling motion of a cylinder. Points ,
, , and
, and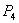 .have different velocities at any instant of time. In fact, the velocity of the point of contact
.have different velocities at any instant of time. In fact, the velocity of the point of contact 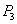 is zero at any instant, if the cylinder rolls without slipping.
Precessional Motion- In precessional motion, the axis of the rotation of body does not remain fixed but rotates about a particular direction sweeping out a cone.
is zero at any instant, if the cylinder rolls without slipping.
Precessional Motion- In precessional motion, the axis of the rotation of body does not remain fixed but rotates about a particular direction sweeping out a cone.
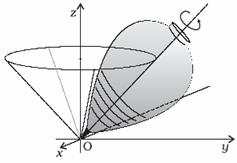 In the above fig.it is shown that axis of rotation of the spinning top moves about z-axis through its point of contact O with the ground sweeping out a cone.
In the above fig.it is shown that axis of rotation of the spinning top moves about z-axis through its point of contact O with the ground sweeping out a cone.
 The above fig shows a rolling motion of a cylinder. Points
The above fig shows a rolling motion of a cylinder. Points In the above fig.it is shown that axis of rotation of the spinning top moves about z-axis through its point of contact O with the ground sweeping out a cone.
In the above fig.it is shown that axis of rotation of the spinning top moves about z-axis through its point of contact O with the ground sweeping out a cone.
Q86. A child rolls down a bowling ball of 6 kg down the alley without slipping at a linear speed of 5m/s. Considering the moment of inertia as 1.5 x 10-2 kg m2 and radius as 0.23 m. Find the total energy.
Solution
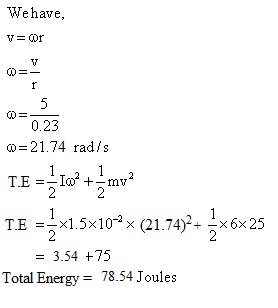
Q87. There are two men standing facing each other on two boats floating on still water at a short distance apart. A rope is held at its ends by both. Explain why the two boats meet at same point when each man pulls the rope separately or both pull together? Will the time taken be different in the two cases? (Neglect Friction)
Solution
As the forces exerted by the two men in boats are the internal forces of the system, therefore, the position of centre of mass remains unchanged. The two boats always meet at the same point which is the centre of mass of the system. It remains unchanged whether both the men pull together or each man pulls separately. However, the boats shall take shorter time to meet when both the men pull together.
Q88. Five forces are separately applied to a flat object lying on a table of negligible friction as shown in figure. The force which will not cause the object to rotate about the centre of the object is 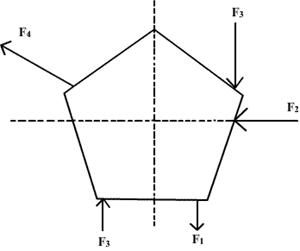

Solution
The line of action of F2 passes through the centre of rotation, and thus cannot produce a torque about the centre (r = 0).
Q89. A child sits stationary at one end of long trolley moving uniformly with speed v on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in the forward direction with speed u. The centre of mass of the system (child + trolley) will move with speed
Solution
The speed of the centre of mass of the system remain unchanged (equal to v) because no external force acts on the system. The force involved such as action and reaction, friction etc when the child runs on the trolley are internal to the (trolley+child) system.
Q90. Three identical uniform rods, each of length 'L' are joined to form a H-shaped frame. What is the distance of the CM of the frame from the CM of the horizontal rod if the C.M. lies at the middle point of the rod?
Solution
Since it is a symmetric frame therefore centre of mass of all the three rods will lie on the horizontal axis, passing through the CM of the middle rod.
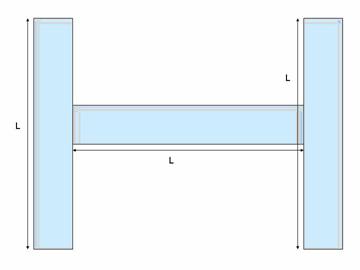 If mass of each rod be M and origin shifts to the CM of the middle rod,
Coordinates of Centre of Mass of all he three rods = (-L/2, 0), (0, 0) and (+L/2, 0).
Therefore, Coordinates of the centre of mass of the H-shaped body are
If mass of each rod be M and origin shifts to the CM of the middle rod,
Coordinates of Centre of Mass of all he three rods = (-L/2, 0), (0, 0) and (+L/2, 0).
Therefore, Coordinates of the centre of mass of the H-shaped body are
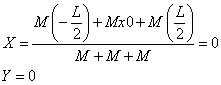 Therefore the distance is zero.
It has been clear that, the center of mass of this symmetrical structure will be at its center. And since the origin is at the center of this structure, the center of mass coordinates are X=0 and Y=0.
Therefore the distance is zero.
It has been clear that, the center of mass of this symmetrical structure will be at its center. And since the origin is at the center of this structure, the center of mass coordinates are X=0 and Y=0.
 If mass of each rod be M and origin shifts to the CM of the middle rod,
Coordinates of Centre of Mass of all he three rods = (-L/2, 0), (0, 0) and (+L/2, 0).
Therefore, Coordinates of the centre of mass of the H-shaped body are
If mass of each rod be M and origin shifts to the CM of the middle rod,
Coordinates of Centre of Mass of all he three rods = (-L/2, 0), (0, 0) and (+L/2, 0).
Therefore, Coordinates of the centre of mass of the H-shaped body are
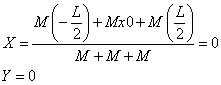 Therefore the distance is zero.
It has been clear that, the center of mass of this symmetrical structure will be at its center. And since the origin is at the center of this structure, the center of mass coordinates are X=0 and Y=0.
Therefore the distance is zero.
It has been clear that, the center of mass of this symmetrical structure will be at its center. And since the origin is at the center of this structure, the center of mass coordinates are X=0 and Y=0.
Q91. Find the centre of mass of three particles forming an equilateral triangle. The masses of the particles are 100g, 150g and 200g respectively. Each side of equilateral triangle is 2 m long.
Solution
 The x coordinate of point B is 2/1 = 1 and
From figure we get that sin 60 ° = BX / OB
i.e. BX = √3 / 2 × 2 =1.732
The X and Y coordinates of point O, A, and B forming the equilateral triangle are respectively (0,0), (2,0), and (1,1.732). Let the masses 100g, 150g, and 200g be located at O,A and B respectively.Then,
The x coordinate of point B is 2/1 = 1 and
From figure we get that sin 60 ° = BX / OB
i.e. BX = √3 / 2 × 2 =1.732
The X and Y coordinates of point O, A, and B forming the equilateral triangle are respectively (0,0), (2,0), and (1,1.732). Let the masses 100g, 150g, and 200g be located at O,A and B respectively.Then,
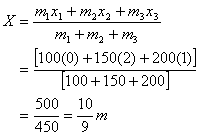
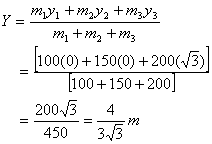 (Here we will replace 1.732 by
(Here we will replace 1.732 by
Q92. If three balls of same radius are placed touching each other on a horizontal surface such that they will form an equilateral triangle, when their centers are joined. What will be the position of the centre of mass of the system?
Solution
The position of the centre of mass of the system will be at the point of intersection of the medians.
Q93. An iron made, regular shaped body moves with an initial velocity of “v” on an inclined plane. It reaches to a maximum height of 7 v 2/10 g.What is the geometrical shape of the body?
Solution
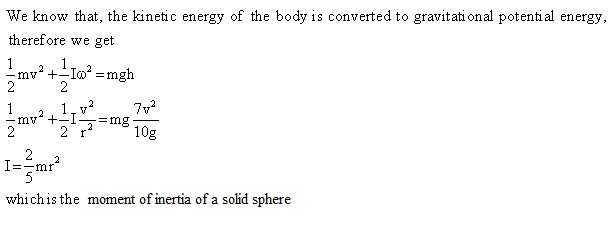
Q94. What do you mean by Torque?
Solution
Torque is the rotational analogue of force which gives us the turning effect of the force about a fixed point or axis. It is measured by the product of the magnitude of force and perpendicular distance of the line of action of force from the axis of rotation.
Q95. When will you say that a body is in partial equilibrium?
Solution
A body is said to be in partial equilibrium when it is in translation equilibrium but not in rotational equilibrium, or it is in rotational equilibrium and not in translational equilibrium.
Q96. What is the physical meaning of Torque?
Solution
Torque τ is defined as a quantity in rotational motion, which when multiplied by a small angular displacement gives us work done in rotational motion. This quantity corresponds to force in linear motion, which when multiplied by a small linear displacement gives us work done in linear motion.
Q97. Two children sit on a see-saw which is 6 m long and pivoted on an axis at its center. The first child has a mass m1 of 20 kg and sits at the left end of the see-saw, while the second child has a mass m2 of 40 kg and sits somewhere on the see-saw to the right of the axis. At what distance from the axis should the second child sit to keep the see-saw horizontal? 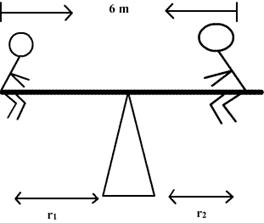

Solution
For the see-saw to remain horizontal, the torque on the left must equal the torque on the right. Therefore,
Torque on the left = Torque on the right
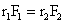 As the forces acting on the see-saw on either side are just the weight mg of each child, and r1 = 3 m, so
As the forces acting on the see-saw on either side are just the weight mg of each child, and r1 = 3 m, so
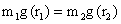 On solving for r2 we get
On solving for r2 we get
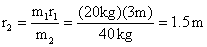 towards fulcrum.
towards fulcrum.
Q98. A planet revolves around a massive star in a highly elliptical orbit. Is its angular momentum constant over the entire orbit?
Solution
Yes, angular momentum of the planet is constant over the entire orbit. This is because revolution of planet around the star is under the effect of gravitational force between the star and the planet. This is a radial force whose torque is zero. Therefore, angular momentum of the planet is a constant (vector), whatever is the nature of the orbit.
Q99. Two blocks A and B of equal mass are released on two sides of a fixed wedge C as shown in figure. Find the acceleration of centre of mass of blocks A and B. neglect friction. 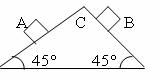

Solution
Acceleration of both the blocks will be g sin45o or 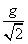 at right angles to each other.
at right angles to each other.
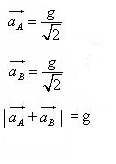 Now,
Now, 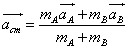
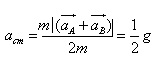 Acceleration is 1/2 g downwards.
Acceleration is 1/2 g downwards.
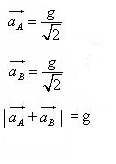 Now,
Now, 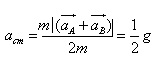 Acceleration is 1/2 g downwards.
Acceleration is 1/2 g downwards.
Q100. An isolated particle of mass m is moving in a horizontal plane (x,y) along the x axis at a certain height above the ground. It suddenly explodes into two fragments of masses m/4 and 3m/4. An instant later, the smaller fragments is at y = +15 cm. The larger fragment at this instant is at
Solution

Q101. When a shell was following a parabolic path in the air, it explodes somewhere in its flight. The centre of mass of fragments will continue to move in
Solution
The total external force (force of gravity) acting on the shell is same before and after the explosion. Therefore the centre of mass of the fragments under the influence of the external force follows the same parabolic path.
Q102. A flywheel has moment of inertia 2 kgm2. What constant torque is required to increase its speed from 4 rps to 12 rps in 8 sec?
Solution

Q103. A wheel rotates with a constant acceleration of 2.0 rad/s2 . If the wheel starts from rest, the number of revolutions it makes in the first ten seconds will be approximately:
Solution

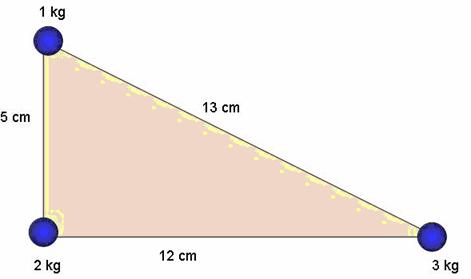
Q104. Three particles of masses 1 kg, 2 kg and 3 kg are placed at the three corners of a right angled triangle of sides 5 cm, 12 cm and 13 cm. Locate the centre of mass of the system.

Solution
Let us take 12 cm line as the X-axis and the 5 cm line as the Y-axis.
The coordinates of the three particles are as follows:
1kg (0, 5), 2kg (0, 0) and 3 kg (12, 0).
 Therefore the x-coordinate of the centre of mass is
Therefore the x-coordinate of the centre of mass is
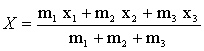 on substitution,
on substitution,  Similarly the y coordinate is
Similarly the y coordinate is
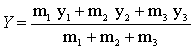 on substitution,
on substitution, Therefore the coordinates of the centre of mass are
Therefore the coordinates of the centre of mass are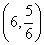 .
.
 Therefore the x-coordinate of the centre of mass is
Therefore the x-coordinate of the centre of mass is
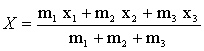 on substitution,
on substitution,  Similarly the y coordinate is
Similarly the y coordinate is
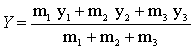 on substitution,
on substitution, Therefore the coordinates of the centre of mass are
Therefore the coordinates of the centre of mass are
Q105. In the HCL molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 angstrom (1 angstrom = 10-10 m). Find the approximate location of the centre of mass of the molecule, given that a chlorine atom is about 35.5 times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus.
Solution
Let us choose the origin at the H atom. Then, xH = 0
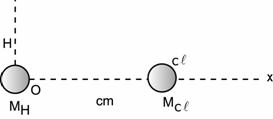 Using the formula for centre of mass for a system of two particles
Using the formula for centre of mass for a system of two particles

 On substituting the values, we get:
On substituting the values, we get:

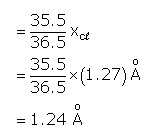 Therefore, the centre of mass of the molecule is
Therefore, the centre of mass of the molecule is 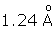 from the position of H-atom.
from the position of H-atom.
 Using the formula for centre of mass for a system of two particles
Using the formula for centre of mass for a system of two particles

 On substituting the values, we get:
On substituting the values, we get:

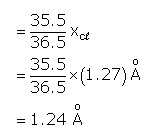 Therefore, the centre of mass of the molecule is
Therefore, the centre of mass of the molecule is
Q106. Ram tied a stone at the end of a thread. In 10 s with a uniform angular acceleration he rotates the stone from a speed of 120 rpm to a speed of 180 rpm. Find the angular acceleration and angular displacement.
Solution
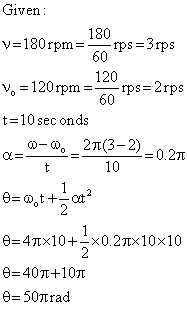
Q107. What will be the radius of gyration of a thin rod of length l about an axis passing through one of its end and perpendicular to the length?
Solution
The moment of inertia of a thin rod about an axis passing through one of its end and perpendicular to the length is given by
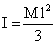 (1)
Also, if M and K be the mass of the body and radius of gyration respectively, moment of inertia of the above said body will be given by
(1)
Also, if M and K be the mass of the body and radius of gyration respectively, moment of inertia of the above said body will be given by
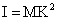 (2)
Comparing eq. (1) and (2) we get,
(2)
Comparing eq. (1) and (2) we get,
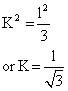
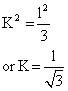
Q108. What will be the position of centre of mass in case of a plane lamina of the shape of a rectangle?
Solution
It will be at the point of intersection of two diagonals.
Q109. Calculate the moment of inertia of a uniform circular disc of radius R and mass M about an axis a. passing through its centre and normal to the discb. passing through a point on its edge and normal to the disc.It is given that moment of inertia of the disc about any of its diameter is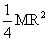
Solution
We have, moment of inertia of the disc about its diameter, Id = 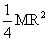 Let us suppose that x and y-axis are the two perpendicular diameters of the disc. Then,
Ix = Iy = Id =
Let us suppose that x and y-axis are the two perpendicular diameters of the disc. Then,
Ix = Iy = Id = 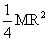 a. If
a. If 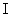 is moment of inertia of the disc about an axis passing through its centre and normal to its plane, then according to the theorem of perpendicular axis,
is moment of inertia of the disc about an axis passing through its centre and normal to its plane, then according to the theorem of perpendicular axis,
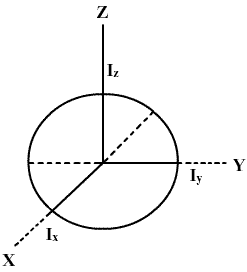 Iz = Ix + Iy =
Iz = Ix + Iy =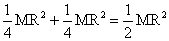 b. If ICD is the moment of inertia of the disc about an axis passing through a point on its edge and normal to its plane, then according to theorem of parallel axis,
b. If ICD is the moment of inertia of the disc about an axis passing through a point on its edge and normal to its plane, then according to theorem of parallel axis,
 CD =
CD =  z + Mh2 and h = R
z + Mh2 and h = R
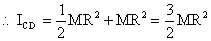
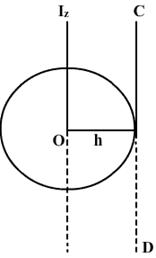
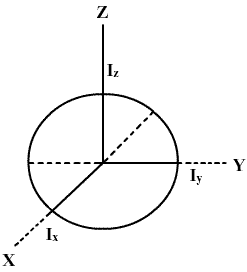 Iz = Ix + Iy =
Iz = Ix + Iy =
Q110. Describe the significance of the concept of centre of mass.
Solution
Centre of mass of a system is a point where the total mass of the system is supposed to be concentrated and all the external forces act there. So, the description of motion becomes easier in terms of centre of mass of the system. Thus centre of mass enables us
To apply Newton's law of motion to extended bodies without difficulty
To apply law of conservation of momentum/energy to a single particle rather than individual particles.
Q111. Explain if the ice on the polar caps melts, how will it affect the rotation of earth?
Solution
The centripetal force required for the rotation of the earth is due to the gravitational pull of sun. Hence an extra torque is not required for it. Hence earth’s angular momentum is constant.
But if the ice of the ice cap melts, it will cause a rise in the sea level and the earth’s mass will be redistributed. It will cause an increase in the moment of inertia of earth, thereby decreasing the angular velocity of earth.
On, applying law of conservation of angular momentum:
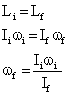 Hence, increase in the MI of the Earth, due to melting of ice, will decrease angular velocity. Due to which the earth will rotate slower.
Hence, increase in the MI of the Earth, due to melting of ice, will decrease angular velocity. Due to which the earth will rotate slower.
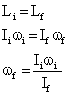 Hence, increase in the MI of the Earth, due to melting of ice, will decrease angular velocity. Due to which the earth will rotate slower.
Hence, increase in the MI of the Earth, due to melting of ice, will decrease angular velocity. Due to which the earth will rotate slower.
Q112. Find the angular acceleration of a rod of 1 kg and length 1 m on which a torque of 12 Nm is applied.
Solution
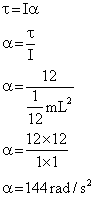
Q113. When will be the torque due to force maximum and minimum.
Solution
We know that,
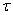 = r F sin Φ
Torque will be maximum, when sin Φ = max = +1 .Therefore Φ = 90 ° i.e when the force is applied in a direction perpendicular to
= r F sin Φ
Torque will be maximum, when sin Φ = max = +1 .Therefore Φ = 90 ° i.e when the force is applied in a direction perpendicular to  .
Torque will be minimum, when Φ = 0° or 180° ,sin Φ =sin 0° or sin 180° =0 i.e when the force is applied parallel to the direction of
.
Torque will be minimum, when Φ = 0° or 180° ,sin Φ =sin 0° or sin 180° =0 i.e when the force is applied parallel to the direction of  .
As sin 0° = 0
.
As sin 0° = 0
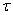 = r F x 0 = 0
= r F x 0 = 0
 .
Torque will be minimum, when Φ = 0° or 180° ,sin Φ =sin 0° or sin 180° =0 i.e when the force is applied parallel to the direction of
.
Torque will be minimum, when Φ = 0° or 180° ,sin Φ =sin 0° or sin 180° =0 i.e when the force is applied parallel to the direction of  .
As sin 0° = 0
.
As sin 0° = 0
Q114. What is angular momentum?
Solution
The turning movement of a particle about the axis of rotation is called angular momentum and is measured as the product of the linear momentum and the perpendicular distance of its line of action from the axis of rotation.
In vector form, 

Q115. Why does a ballet dancer fold her arms while spinning?
Solution
Ballet dancer while performing, fold her arms to spin faster. This act involves the use of rotational motion i.e. when the dancer folds her arm while spinning, the moment of inertia decreases. Since we know
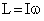 To keep the L constant the angular velocity
To keep the L constant the angular velocity 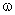 increases. And hence ballet dancer spins faster there by enhancing the performance.
increases. And hence ballet dancer spins faster there by enhancing the performance.
Q116. Explain that Torque is only due to transverse component of force. Radial component has nothing to do with torque.
Solution
As we know that
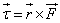
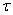 = r F sinΦ----------------------------------------(1)
The figure given below shows the relative orientation of
= r F sinΦ----------------------------------------(1)
The figure given below shows the relative orientation of 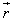 and
and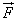 .
.
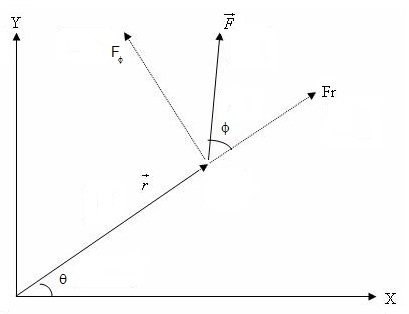 Resolve
Resolve  into two rectangular components:
i) F r= F cos Φ
= radial component of
into two rectangular components:
i) F r= F cos Φ
= radial component of  ii) FΦ= F sin Φ = Transverse component of
ii) FΦ= F sin Φ = Transverse component of From e q(1)
From e q(1)
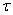 = r (F sinΦ)
= r F Φ
i.e Torque of a force is given by the product of transverse component of force and perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation. The radial component has no role play in torque.
= r (F sinΦ)
= r F Φ
i.e Torque of a force is given by the product of transverse component of force and perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation. The radial component has no role play in torque.
 Resolve
Resolve
Q117. Show that the velocity of centre of mass of an isolated system remains constant?
Solution
If the total mass M of the system is concentrated at the centre of mass, whose position vector is 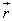 , then
, then
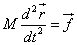
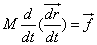 But
But 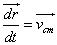 = velocity of cetre of mass of the system
Therefore,
= velocity of cetre of mass of the system
Therefore,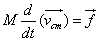 For an isolated system, no external forces are acting, and the internal forces cancel out in pairs. Therefore, total force
For an isolated system, no external forces are acting, and the internal forces cancel out in pairs. Therefore, total force 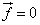 =>
=> 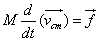 =0
As M
=0
As M 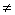 0, therefore
0, therefore 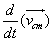 = 0
Or,
= 0
Or, 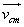 = constant
It means that centre of mass of an isolated system has a constant velocity. It implies that if centre of mass of an isolated system is already at rest, it remains at rest. If the centre of mass is moving with a certain velocity in a certain directions it continues to move with the same velocity in the same direction. Under no circumstances, the velocity of centre of mass of an isolated system can undergo a change.
= constant
It means that centre of mass of an isolated system has a constant velocity. It implies that if centre of mass of an isolated system is already at rest, it remains at rest. If the centre of mass is moving with a certain velocity in a certain directions it continues to move with the same velocity in the same direction. Under no circumstances, the velocity of centre of mass of an isolated system can undergo a change.
Q118. Is it necessary that there should be mass at the centre of mass of a system?
Solution
No, there need not be any mass at the centre of mass of a system. For example centre of mass of a ring lies at its centre where there is no mass.
Q119. What do you mean by radius of gyration? Is radius of gyration a constant quantity?
Solution
For any body rotating about a given axis, it is possible to find a radial distance from the axis where, if the whole mass of the body is supposed to be concentrated, its moment of inertia remain unchanged. This radial distance is called radius of gyration.
Radius of gyration is not a constant quantity but its value changes with change of location of axis of rotation.Its value depends on shape and size of the body, position and configuration of the axis of rotation and also on distribution of mass of the body with respect to the axis of rotation.
Q120. For a rigid body to be in rotational equilibrium, prove that the sum of all the external torques acting on it is zero.
Solution
As we know that rotational motion of a rigid body is governed by the following equation: 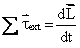
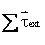 is the sum of all the external torques acting on the body, and
is the sum of all the external torques acting on the body, and 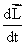 represents the rate of change of angular momentum.
For equilibrium,
represents the rate of change of angular momentum.
For equilibrium, 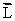 must have fixed value.
must have fixed value.
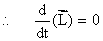
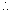
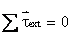
Q121. Show that angular momentum of a satellite of mass m1 revolving around earth of mass M in an orbit of radius r is 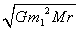
Solution
As we know that, a satellite revolves around the earth under gravitational pull, which provides the necessary centripetal force
i.e 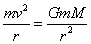
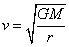 Angular momentum of satellite,
L = m1v r
=
Angular momentum of satellite,
L = m1v r
=  =
=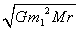
 =
=
Q122. What would be the velocity of centre of mass of the system if the resultant of all external forces acting on it is zero?
Solution
The velocity of centre of mass remains constant if the resultant of all external forces acting on it is zero and so does the linear momentum of the system.
Q123. If a particle is rotating along a circular path in XY plane. What will be the direction of angular momentum, why?
Solution
The angular momentum vector will be directed parallel to Z-axis because 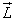 is always perpendicular to the plane containing
is always perpendicular to the plane containing 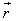 and
and 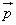 in accordance with right handed screw rule.
in accordance with right handed screw rule.
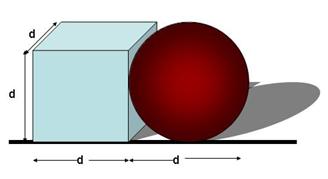
Q124. A cube of side 'd' and a sphere of diameter 'd' are kept in contact as shown here. The density of the material and the thickness are same every where. Locate the position of the centre of mass of the composite system.

Solution
Since the cube and sphere are symmetrical objects; therefore their C.M. will lie at their geometrical centers only.
Taking centre of the cube as the origin, the coordinates of the C.M. of cube will be (0, 0) and sphere will be (d, 0).
 .
Let the mass per unit volume be
.
Let the mass per unit volume be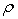 .
Then the mass of the cube
.
Then the mass of the cube 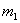 =
= 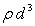 And mass of the sphere
And mass of the sphere
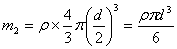 Therefore the coordinates of the centre of mass of the composite system are
Therefore the coordinates of the centre of mass of the composite system are
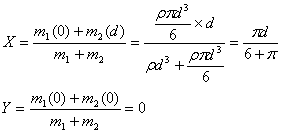 Thus we have,
Thus we have, 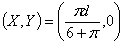
 .
Let the mass per unit volume be
.
Let the mass per unit volume be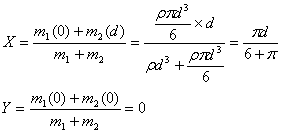 Thus we have,
Thus we have,
Q125. An Earth satellite is moving around the earth in a circular orbit. In such case, what is conserved?
Solution
Angular momentum is conserved as no external torque is acting in the motion of satellites around the Earth.
Q126. Two bodies of masses m1 and m2 are connected to the ends of a massless cord and allowed to move as shown. If the pulley is both massless and frictionless, find the acceleration of the centre of mass. 

Solution
Let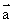 is the acceleration of m1 and
is the acceleration of m1 and 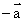 is the acceleration of m2.
We know that,
is the acceleration of m2.
We know that,
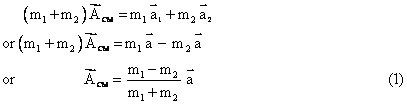 But in a connected body problem we have,
But in a connected body problem we have,
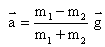 On substituting the value of
On substituting the value of 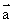 in eq. (1) we get,
in eq. (1) we get,
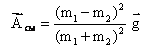
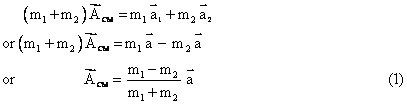 But in a connected body problem we have,
But in a connected body problem we have,
Q127. If the angular position of a body under circular motion is given by the equation:  Find the expression for angular velocity and angular displacement.
Find the expression for angular velocity and angular displacement.
Solution
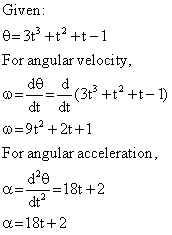
Q128. Calculate the area of a parallelogram whose adjacent sides are given by the vectors :


Solution
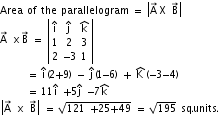
Q129. A body of mass 45 kg is moving with constant velocity 5 m/s parallel to x axis. The distance traveled by the body from the origin during its motion is 300 m. what will the angular momentum of the body about the origin?
Solution
m = 45 kg, v = 5 m/s, r = 300m
L = mvr
= 45 x 5 x 300
= 67500 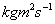
Q130. Fly wheel rotates at a speed of 360 rpm and at a rate of 6 rad /s2 it slows down. Calculate the time after which it will stop.
Solution
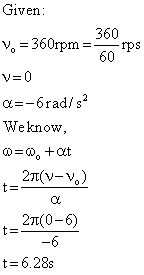
Q131. Why in diatomic molecule, the atom of larger mass revolves in a circular path of lesser radius about the centre of mass, while the atom of smaller mass revolves in circular path of greater radius.
Solution
In the diatomic molecule, in its stable equilibrium state, the two atoms lie at a certain distance 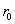 , called bond length. The centre of mass of a system of two particles divides the distance between the two particles in the inverse ratio of their masses. If
, called bond length. The centre of mass of a system of two particles divides the distance between the two particles in the inverse ratio of their masses. If 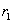 and
and 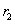 are the distance of the atoms A and B from their centre of mass C.
are the distance of the atoms A and B from their centre of mass C.
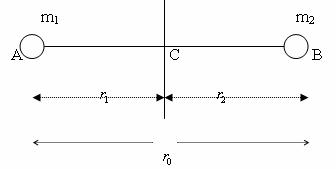 Since the centre of mass coincides with the axis of rotation:
Since the centre of mass coincides with the axis of rotation:
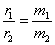
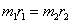 -----------(1)
since,
-----------(1)
since,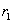 +
+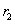 =
=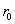 Therefore,
Therefore,
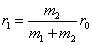 -----------(2)
-----------(2)
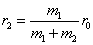 ------------(3)
The diatomic molecule cannot form a stable system, if the two atoms are at rest.
It is because the atoms will get pulled towards each other. In order to achieve stability, the two atoms revolve about their centre of mass. If
------------(3)
The diatomic molecule cannot form a stable system, if the two atoms are at rest.
It is because the atoms will get pulled towards each other. In order to achieve stability, the two atoms revolve about their centre of mass. If 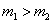 from e q (2) and (3)
It follows
from e q (2) and (3)
It follows 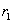 <
<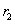 .
This implies that the atom of larger mass revolves in a circular path of lesser radius about the centre of mass, while the atom of smaller mass revolves in circular path of greater radius.
.
This implies that the atom of larger mass revolves in a circular path of lesser radius about the centre of mass, while the atom of smaller mass revolves in circular path of greater radius.
 Since the centre of mass coincides with the axis of rotation:
Since the centre of mass coincides with the axis of rotation:
Q132. What percentage of total mechanical energy is translational when a spherical ball is rolled without sliding?
Solution

Q133. Is Torque a scalar or vector quantity? If it is a vector, what rule is used to determine its direction?
Solution
Torque is a vector quantity i.e
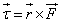 .
Its direction is determined by right handed screw rule or right handed thumb rule and is perpendicular to plane containing
.
Its direction is determined by right handed screw rule or right handed thumb rule and is perpendicular to plane containing 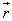 and
and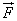 .
.
Q134. A projectile projected at a certain angle with the horizontal hits the ground at P. However, if this particle explodes at the highest point into two pieces of equal mass. One piece falls to the ground vertically downwards at Q, while the other travels horizontally and hit the ground at R. What is the distance of R from P?
Solution
In the explosion, only the internal forces are involved and internal forces can not change the motion of centre of mass, So after explosion will takes place, the centre of mass continue to move along the same parabolic path. Since the two fragments are of equal mass, therefore, P would be the mid way between Q and R.
Q135. What is the ratio of the rotational kinetic energy and translational kinetic energy of disk moving about the axis passing through its centre perpendicular to the plane of the disk?
Solution

Q136. How will you find the centre of mass of a triangular lamina?
Solution
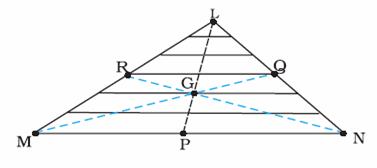 Let the lamina (
Let the lamina (
Q137. Calculate the moment of inertia of a cylinder of length, l = 150 cm and radius, r = 5 cm, density, ρ = 8 g cm-3 about the axis of the cylinder.
Solution
Mass of cylinder = volume x density
=  R2 | x ρ
=
R2 | x ρ
=  x (5)2 x 150 x 8
Moment of inertia,
I =
x (5)2 x 150 x 8
Moment of inertia,
I =  MR2
=
MR2
=  (
( x 25 x 150 x 8)x52
= 1.2 x 106g cm2
x 25 x 150 x 8)x52
= 1.2 x 106g cm2
 R2 | x ρ
=
R2 | x ρ
=  x (5)2 x 150 x 8
Moment of inertia,
I =
x (5)2 x 150 x 8
Moment of inertia,
I =  MR2
=
MR2
=  (
( x 25 x 150 x 8)x52
= 1.2 x 106g cm2
x 25 x 150 x 8)x52
= 1.2 x 106g cm2
Q138. What is the second law of rotational motion?
Solution
According to the second law of rotational motion the angular acceleration of a body is proportional to the torque applied to it.
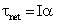
Q139. What will be the position of centre of mass of a two particle system with unequal masses?
Solution
The centre of mass will lie near to the massive particle.
Q140. The mechanical advantage for a lever is greater than one. Comment on the statement.
Solution
The Mechanical Advantage is given by M.A. = 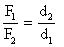 If M.A. > 1 i.e.
If M.A. > 1 i.e. 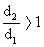
 effort arm > load arm
effort arm > load arm
 small effort can be used to lift a large load.
small effort can be used to lift a large load.
Q141. What is the dimensional formula of Torque? Also write its S.I units?
Solution
Torque= Force x Perpendicular distance
Dimensional formula of torque = [M 1 L 1 T -2] [L]
= [M 1 L 2 T -2]
S.I unit of torque is Nm which is equivalent to joule.
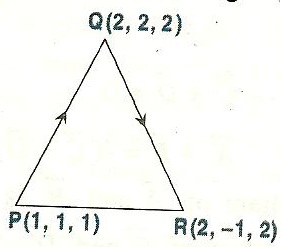
Q142. Find the area of triangle whose vertices are P (1,1,1), Q
(1,1,1), Q  (2,2,2) and R
(2,2,2) and R (2,-1,2).
(2,-1,2).
 (1,1,1), Q
(1,1,1), Q Solution

Q143. A cord is wound around the circumference of a wheel of radius 10 cm. The axis of the wheel is horizontal. A mass of 0.5 kg is attached at the end of the chord and it is allowed to fall from rest. If the weight falls 2 m in 5 s. Calculate the angular acceleration of the wheel. Also find the torque applied by the weight?
Solution
Here
r = 10cm= 0.10m
m= 0.5 kg , u=0
s= 2m, t= 5s
 2 = 0 + 0.5 ×a x 25
2= 0.5 × 25 a
a= 0.16 m/s 2
From a = r α
α = a /r
= 0.16/0.10
= 1.6 rad/s 2
Angular acceleration of the wheel = 1.6 rad/s 2.
Torque applied by the weight
2 = 0 + 0.5 ×a x 25
2= 0.5 × 25 a
a= 0.16 m/s 2
From a = r α
α = a /r
= 0.16/0.10
= 1.6 rad/s 2
Angular acceleration of the wheel = 1.6 rad/s 2.
Torque applied by the weight
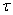 = mgr = 0.5 x 9.8 x 0.10
= 0.49 N m.
= mgr = 0.5 x 9.8 x 0.10
= 0.49 N m.
 2 = 0 + 0.5 ×a x 25
2= 0.5 × 25 a
a= 0.16 m/s 2
From a = r α
α = a /r
= 0.16/0.10
= 1.6 rad/s 2
Angular acceleration of the wheel = 1.6 rad/s 2.
Torque applied by the weight
2 = 0 + 0.5 ×a x 25
2= 0.5 × 25 a
a= 0.16 m/s 2
From a = r α
α = a /r
= 0.16/0.10
= 1.6 rad/s 2
Angular acceleration of the wheel = 1.6 rad/s 2.
Torque applied by the weight
Q144. Calculate the angular momentum with respect to the origin of a particle of mass m = 0.6 kg when it is located at a position 6.0m due South, with speed of 10m/s in direction 30 degrees North of East
Solution
Angular momentum is the cross or a vector product of radius of rotation r and linear momentum p i.e. 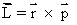


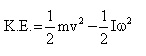





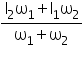
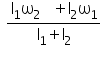
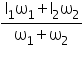
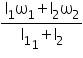














Comments
Post a Comment