Q1. What is meant by an ideal fluid?
Solution
An ideal fluid is the one which is non-viscous, incompressible, and its flow is steady and irrotational.
Q2. Why do carbonated drinks squirt over when shaken and opened?
Solution
A carbonated drink squirts over when opened after shaking because of the internal pressure that has been created inside it due to the shake. When we open it, the internal pressure is higher than the external due to which it squirts.
Q3. Find the gravitational energy per unit mass possessed by 1 kg of water if its total energy per unit mass is 200 J at a point where pressure is 1.96 x 104 Pa and velocity is 0.1 m/s.
Solution
Total energy per unit mass = P/ρ + gh + ½v² (as per Bernoulli's theorem)
200 = 1.96 x 104/103 + gh + ½ (0.1)²
200 = 19.6 + hg + 0.005 = hg + 19.605
Therefore, we have
hg = 200 - 19.605
hg = 180.395 J/Kg
Q4. Two bodies of equal weight and volume and having the same shape, except that one has an opening at the bottom and the other is sealed, are immersed to the same depth in water. Which body requires more work to be immersed and why?
Solution
More work is required in case of the body having hole at its bottom. As the liquid enters the hole, more work is required in compressing the air. So, less work is required in case of the sealed body.
Q5. Dirty or greasy stains cannot be cleared by washing with water and we need detergents. Why?
Solution
Yes dirty or greasy stains cannot be cleared by washing with water and we need detergents for the same because water cannot find contact with the greasy or oily molecules, and hence, it cannot wet the surface.
We use detergents whose molecules are hairpin like in shape. When we dissolve detergents in water the molecules of detergents get attracted to water and when clothes are dipped in such water the hairpin molecules get attached to the grease, and hence, water and greasy dirt interface is formed. Therefore, detergents are used to reduce the surface tension between water and greasy stain. When clothes are rinsed in water the greasy dirt is washed away by running water.
Q6. During flight, the weight of the plane is balanced by
Solution
When the aerofoil moves against the wind, the orientation of the wing relative to flow direction causes the streamlines to crowd together above the wing more than those below it. The flow speed on top is higher than that below it. There is an upward force resulting in a dynamic lift of the wings and this balances the weight of the plane.
Q7. When we close a part of the opening of water tap with our finger, fast jets of water gush through the opening. Explain Why?
Solution
As we close the water-tap with our finger, the area of cross-section of the opening between the finger and tap boundary decreases quite appreciably. In accordance with the equation of continuity (a1v1 = a2v2), the velocity of water increases enormously and fast jets of water gush through the opening.
Q8. What are the limitations of Bernoulli's theorem?
Solution
There are following limitations of Bernoulli's theorem:
(i) In Bernoulli's theorem, the velocity of every particle of liquid across any cross-section is considered uniform which is not correct. The velocity of the particles is different in different layers.
(ii) The loss of energy when the liquid is in motion is not considered while some kinetic energy is converted into heat and is lost.
(iii) The fluids must be incompressible as the elastic energy of the fluid is not taken into account.
Q9. If mustard oil and water are dropped out from a tube separately, the mustard oil comes out later than water. Why?
Solution
If mustard oil and water are dropped out from a tube separately, the mustard oil comes out later than water because the coefficient of viscosity of mustard oil is very large as compared to the coefficient of viscosity of water. Hence, water rushes out quickly than mustard oil.
Q10. Why are oils of different viscosities used in automobiles in different seasons?
Solution
The viscosity of lubricant oils decreases with rise in temperature. Therefore, the oil that is suitable as lubricant in summer, may not be suitable in winter. So, the oils of different viscosities are used as lubricant in different seasons.
Q11. n identical drops (each of radius r) of liquid of surface tension T and density  coalesce to form single drop. The energy released in the processes is converted into kinetic energy. Find the speed of drop.
coalesce to form single drop. The energy released in the processes is converted into kinetic energy. Find the speed of drop.
 coalesce to form single drop. The energy released in the processes is converted into kinetic energy. Find the speed of drop.
coalesce to form single drop. The energy released in the processes is converted into kinetic energy. Find the speed of drop.Solution
Let R is the radius of big drop. Since on coalesce of droplets, the volume of liquid remains constant, therefore

Q12. Explain why, small air bubbles rise slower than the bigger ones through a liquid?
Solution
We know that, the terminal velocity is given as
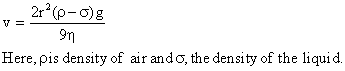 It is clear that the factor (ρ - σ), and hence, v will be negative.
Now, since
It is clear that the factor (ρ - σ), and hence, v will be negative.
Now, since 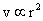 , it follows that air bubbles rise slower than the bigger ones through a liquid.
, it follows that air bubbles rise slower than the bigger ones through a liquid.
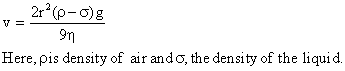 It is clear that the factor (ρ - σ), and hence, v will be negative.
Now, since
It is clear that the factor (ρ - σ), and hence, v will be negative.
Now, since
Q13. A plane is in level flight at constant speed. If the speed of blowing air over the lower wing is 150 km/h and that over the upper wing is 210 km/h, determine the net upward force exerted on the plane. Given area of each wing 20 m². (Take air density to be 1 kg/m³)
Solution
v1 = 150 km/h = 125/3 m/s
v2 = 210 km/h = 175/3 m/s
A = 2 x 20 = 40 m2
According to Bernoulli's theorem, we have
P1 - P2 = 1/2 ρ(v22 - v12)
= 1/2 x 1 [(175/3)2 - (125/3)2] = 1/2 [(30625-15625)/9]
= 15000/18 Pa
Upward force = (P1-P2) x A
= (15000x40)/18 = 33333.33 N
Q14. Velocity of efflux flowing through an orifice at height h below the free surface of liquid is given by
Solution
Velocity of efflux flowing through an orifice at height h below the free surface of liquid is v2 = 2 g h or  .
.
 .
.
Q15. Find the ratio of pressures at height 20 m and 40 m in sea. (Given g = 10 m/s2, density ρ = 1200 kg/m3)
Solution
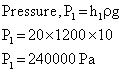
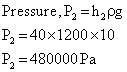

Q16. What happens if the capillary tube is of insufficient height?
Solution
The ascent formula for the liquid is
 where R is the radius of the meniscus and h is the height to which the liquid rises. If the tube is of insufficient height, the liquid will rise to the top of the tube and spread over the brim and the radius of meniscus will adjust to a new value such that Rh remains constant.
where R is the radius of the meniscus and h is the height to which the liquid rises. If the tube is of insufficient height, the liquid will rise to the top of the tube and spread over the brim and the radius of meniscus will adjust to a new value such that Rh remains constant.
 where R is the radius of the meniscus and h is the height to which the liquid rises. If the tube is of insufficient height, the liquid will rise to the top of the tube and spread over the brim and the radius of meniscus will adjust to a new value such that Rh remains constant.
where R is the radius of the meniscus and h is the height to which the liquid rises. If the tube is of insufficient height, the liquid will rise to the top of the tube and spread over the brim and the radius of meniscus will adjust to a new value such that Rh remains constant.
Q17. Derive an expression for excess of pressure inside a soap bubble.
Solution
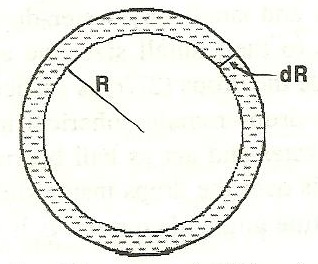 Consider a soap bubble of radius R and surface tension T. There are two free surfaces of soap bubble. Due to surface tension, the molecules on the surface film experience the net force in the inward direction normal to the surface. Therefore, there is more pressure inside than outside.
Let pi be the pressure inside the liquid drop and po be the pressure outside the drop. Therefore, excess pressure inside the liquid drop is
p = pi - po
Due to excess pressure inside the liquid drop, the free surface of the drop will experience the net force in the outward direction due to which the drop will expand.
Let the free surfaces be displaced by dR under isothermal conditions. Therefore, excess pressure does the work in displacing the surface and that work will be stored in the form of potential energy.
The work done by excess pressure in displacing the surface is
dW = force × displacement
= (excess pressure x Surface area × displacement of surface)
Consider a soap bubble of radius R and surface tension T. There are two free surfaces of soap bubble. Due to surface tension, the molecules on the surface film experience the net force in the inward direction normal to the surface. Therefore, there is more pressure inside than outside.
Let pi be the pressure inside the liquid drop and po be the pressure outside the drop. Therefore, excess pressure inside the liquid drop is
p = pi - po
Due to excess pressure inside the liquid drop, the free surface of the drop will experience the net force in the outward direction due to which the drop will expand.
Let the free surfaces be displaced by dR under isothermal conditions. Therefore, excess pressure does the work in displacing the surface and that work will be stored in the form of potential energy.
The work done by excess pressure in displacing the surface is
dW = force × displacement
= (excess pressure x Surface area × displacement of surface)
 Increase in potential energy is
Increase in potential energy is
 From (1) and (2), we get
From (1) and (2), we get

Q18. What is the weight of the body, when it falls with terminal velocity through a viscous medium?
Solution
When a body falling through a viscous medium attains terminal velocity, the apparent weight of the body is balanced by the viscous force due to the medium. Therefore, the weight of a body falling with terminal velocity is zero.
Q19. Determine the height of purple liquid in a U tube. Density of purple liquid is 0.7 g/cc , density of blue liquid = 1.4 g/cc , density of mercury = 13.6 g/cc. 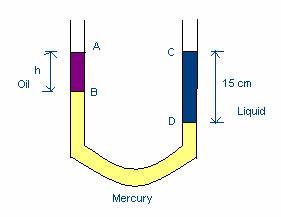

Solution
Considering equilibrium state, the pressure of liquids at the same level must be equal.
Pressure due to h cm of purple liquid + pressure due to (15-h) cm of mercury =
pressure of 15 cm of blue liquid.


Q20. Suppose there are two bubbles B1 and B2. The excess pressure inside B1 is twice the excess pressure in B2. Find the ratio between the volumes of the two bubbles.
Solution

Q21. What will be the pressure in sea at a depth of 20 m? (Given g = 10 m/s2, density ρ = 1200 kg/m3)
Solution
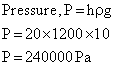
Q22. Explain why, the lubricant oils used in our automobiles should be of high viscosity?
Solution
When oil is used as a lubricant in machines, it forms a thin layer over the metallic parts of the machinery. Hence, during normal working of the machinery, the metallic parts do not come in direct contact with each other. Now, for the oil layer to be effective as a lubricant for a long time, the oil should be of high viscosity.
Q23. Distinguish between Turbulent and Streamline flow.
Solution
S. No
Turbulent flow
Streamline Flow
1.
The velocity of liquid is high and unsteady.
The velocity of liquid is low and steady.
2.
Velocity of liquid is greater than the critical velocity.
Velocity of liquid is below its critical velocity.
3.
The velocity of every particle of liquid keeps on changing at every instant.
The velocity of every particle of liquid crossing a particular point is same.
Q24. On the basis of equation of continuity show that deep water runs slow.
Solution
Consider a part of a river, which has got different depths d1 and d2 at the two places say A and B respectively. We assume that width b of the river is same throughout.
Area of cross-section of the river at A is a1 = bd1
And area of cross section of the river at B is a2 = bd2
If v1 and v2 are the values of velocity of flow of water at A and B respectively, then according to the equation of continuity, we have
a1v1 = a2v2
bd1v1 = bd2v2
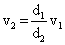 Since d2 >d1, v2 < v1, it follows that the slow water runs deep.
Since d2 >d1, v2 < v1, it follows that the slow water runs deep.
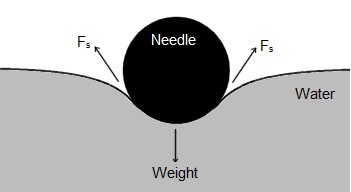
Q25. When a sewing needle is gently placed on the surface of water, it floats. Why?
Solution
When the needle is gently placed on the surface of water, it gets slightly depressed. The force due to surface tension on depressed curved surface is inclined upwards, whose resultant is vertically upwards. This resultant balances the weight of the needle. Hence, the needle floats on the surface.

Q26. Broad straps are provided for bags or suitcases. Why?
Solution
Pressure is inversely proportional to the area. Hence, bags and suitcases have broad straps so as to increase the area and reduce pressure exerted by them on shoulders or hands, thereby making it easier for us to carry the luggage.
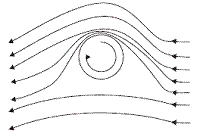
Q27. If a ball is thrown and given a spin, then the path of the ball is curved more than a usual spin free ball. Why?
Solution
A ball which is spinning drags air along with it. If the surface is rough more air will be dragged. The layer above the ball moves in a direction opposite to that of a spinning ball, so the resultant velocity decreases, and hence, pressure increases in accordance with Bernoulli's principle.
The layer below the ball moves in the direction of spin and the resultant velocity increases thereby decreasing the pressure. Due to the difference of pressure on the two sides of the ball, the ball curves downward in the direction of spin.

Q28. What is the radius of new bubble formed if two bubbles of radii 2 cm and 1.5 cm coalesce?
Solution

Q29. What are the factors on which the pressure in the liquid at rest depends?
Solution
The pressure in the liquid at rest depends on:
(i) Depth of liquid
(ii) Density of liquid
(iii) Acceleration due to gravity
Q30. What would happen to the equilibrium of a physical balance when air is blown below one of the pans?
Solution
When air is blown below one of the pans, there will be an increase in air velocity due to which the pressure decreases, and hence, the pan goes down.
Q31. When we swim under water, pressure on our body increases as we go deeper, but yet our body is not crushed due to this pressure. Why?
Solution
When we swim under water, our body is not crushed due to increasing pressure as we go deeper because our body tries to compensate for this pressure by creating an internal pressure which balances this external pressure. But, as we go deeper and deeper, there will be a depth at which our body feels uncomfortable resulting in serious injuries.
Q32. Calculate the gravitational potential energy per unit mass possessed by water if the height of the water level from the ground is 0.20 m?
Solution
h = 0.2 m
Gravitational potential energy per unit mass = gh
= 9.8 x 0.2
= 1.96 J /kg
Q33. Explain why is the velocity of water in a river less on the banks and large in the middle?
Solution
Due to large force of adhesion between the water streams and the bank of the river, the velocity of water is quite small near the bank as compared to that in the middle of it.
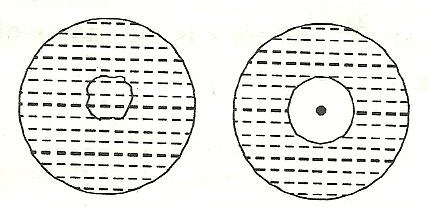
Q34. If we place a cotton thread loop on a soap film gently and prick the film within the loop then what shape will the thread loop acquire?
Solution
The loop of thread acquires a circular shape, because for a given perimeter, a circle has maximum area, and therefore, rest of the soap film will acquire minimum surface area.

Comments
Post a Comment