Q1. What will be the period of oscillation of a simple pendulum of length 100 cm in a spaceship in a geostationary orbit?
Solution
In any satellite orbiting the Earth (in any orbit), the condition of weightlessness exists (i.e. effective g = 0). Hence, the pendulum does not oscillate and its period is therefore infinity.
Q2. Which of the following functions of time represent :
(a) simple harmonic
(b) periodic but not simple harmonic
(c) non-periodic motion?
where k is a real positive constant.
(i) sin kt+cos kt
(ii) 2 sin2kt
(iii) e-kt
(iv) log kt
Solution

Q3. Two identical, springs each of spring factor K, may be connected in the following different ways..
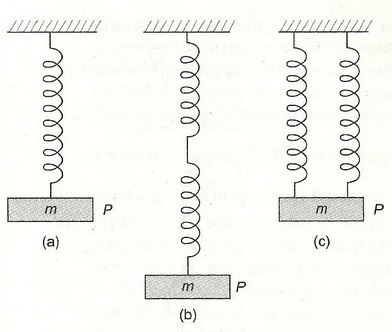 Deduce the spring factor for oscillations of the body P of mass m in each case.
Deduce the spring factor for oscillations of the body P of mass m in each case.
 Deduce the spring factor for oscillations of the body P of mass m in each case.
Deduce the spring factor for oscillations of the body P of mass m in each case.Solution
(a) Let the mass of the body P be m. Suppose an extension x is produced in the spring when a force mg is applied to it. The equilibrium position is given by:
F = mg = kx ......(i)
The time period in this case is given by,


Q4. Two bodies P and Q of equal masses are suspended from two separate springs of constants K1 and K2 respectively. If the two bodies oscillate vertically such that their maximum velocities are equal, then what is the ratio of the amplitudes of vibration of P and Q?
Solution
Frequency of oscillation of body P


Q5. A particle is executing simple harmonic motion. What is phase relationship between velocity and acceleration?
Solution
Let the position of particle be given by 

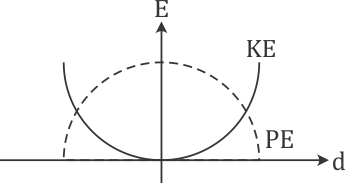
Q6. For a simple pendulum, a graph is plotted between its kinetic energy (KE) and potential energy (PE) against its displacement d. Which one of the following represents these correctly?
(graphs are schematic and not drawn to scale)
Solution
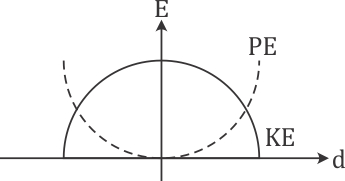 Potential energy is maximum at the extremes while kinetic energy is maximum at the mean position.
Potential energy is maximum at the extremes while kinetic energy is maximum at the mean position.
Q7. Write the values of amplitude and angular frequency for the following simple harmonic motion : y = 0.2 sin ( 99t + 0.36)
The various quantities are in the SI units.
Solution
We have, y = 0.2 sin (99t + 0.36)
Comparing it with
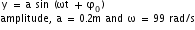
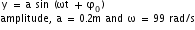
Q8. A particle is executing simple harmonic motion. What is the ratio potential energy to kinetic energy when the displacement is 0.6A, where A is the amplitude of oscillation?
Solution

Q9. A body oscillates simple harmonically according to equation y = 5 cos ( cm. What is displacement, velocity and acceleration at t = 3s.
cm. What is displacement, velocity and acceleration at t = 3s.
 cm. What is displacement, velocity and acceleration at t = 3s.
cm. What is displacement, velocity and acceleration at t = 3s.Solution
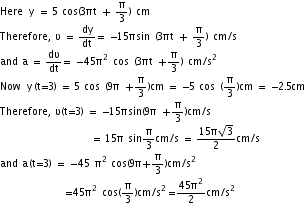
Q10. A sphere is hung at the end of a wire, and 30o rotation of the sphere about the wire generates a restoring torque of 4.6 Nm. If the moment of inertia of the sphere is 0.082 kg m2, deduce the frequency of angular oscillations.
Solution
Angular displacement, 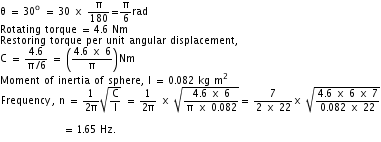
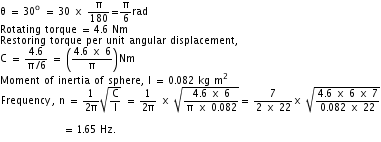
Q11. If y =  sin wt -
sin wt -  cos wt, find the amplitude of motion.
cos wt, find the amplitude of motion.
 sin wt -
sin wt -  cos wt, find the amplitude of motion.
cos wt, find the amplitude of motion.Solution
Given : y =  sin wt -
sin wt -  cos wt .................(i)
Put
cos wt .................(i)
Put  = r cos
= r cos ,
,  = r sin
= r sin Therefore, r2 (1) =
Therefore, r2 (1) =  +
+  =
=  or r =
or r =  Therefore, y = r sin (wt -
Therefore, y = r sin (wt -  ) ........................(ii)
y =
) ........................(ii)
y =  sin (wt -
sin (wt -  )
Therefore, equation (i) represents SHM and its amplitude is
)
Therefore, equation (i) represents SHM and its amplitude is .
.
 sin wt -
sin wt -  cos wt .................(i)
Put
cos wt .................(i)
Put  = r cos
= r cos ,
,  = r sin
= r sin Therefore, r2 (1) =
Therefore, r2 (1) =  +
+  =
=  or r =
or r =  Therefore, y = r sin (wt -
Therefore, y = r sin (wt -  ) ........................(ii)
y =
) ........................(ii)
y =  sin (wt -
sin (wt -  )
Therefore, equation (i) represents SHM and its amplitude is
)
Therefore, equation (i) represents SHM and its amplitude is .
.
Q12. A tray of mass 9 kg is supported by two springs, each of force constant K as shown in the figure. On pressing the tray slightly downwards and then releasing it, it executes SHM of period 1s. When a block of mass M1 is placed in the tray, the period increases by 2s. Calculate the mass of the block.
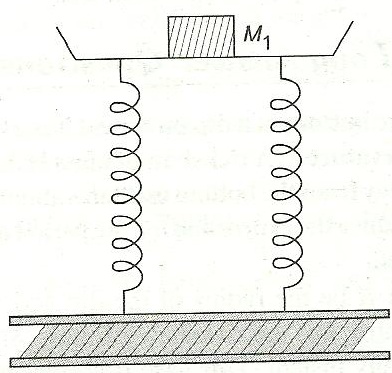

Solution
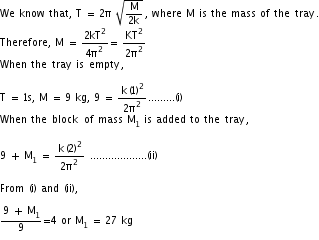
Q13. Why is loud sound heard at resonance?
Solution
At resonance compression falls on compression and rarefaction falls over rarefaction, due to which amplitude of vibration of particle increases. Since I is proportional to A2, therefore maximum sound is heard at resonance.
Q14. At a certain speed of a bus, the body of the bus starts vibrating strongly. Why?
Solution
At certain speed of bus, the frequency of the bus engine becomes equal to the natural frequency of its frame and hence resonant vibration of frame takes place, therefore bus begins to vibrate strongly.
Q15. Two identical springs of force constant k each are connected in series. What will be the spring factor of the combination when they are connected in
(i) Series
(ii) Parallel
Solution
(i) Series combination:
 (ii) Parallel combination:
(ii) Parallel combination:

 (ii) Parallel combination:
(ii) Parallel combination:

Q16. How earthquakes some times cause disaster?
Solution
When the waves produced during earthquake have same frequency as that of the natural frequency of buildings, the resonance takes place and the building start vibrating with large amplitude and the amplitude is to large that the buildings collapse. In this way the earthquakes causes big disaster.
Q17. A vertical U-tube of uniform cross-section contains water up to a height of 20 cm. Calculate the time-period of the oscillation of water when it is disturbed.
Solution
The length of the liquid column, L = 2 x 20 = 40 cm
Time period of oscillation,
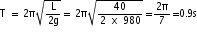
Q18. Will a pendulum gain or lose time, when taken to the top of a mountain?
Solution
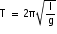 On taking the pendulum to the top of a mountain, g will decrease, therefore, T will increase. The pendulum will take more time to complete one vibration, i.e., it will lose time.
On taking the pendulum to the top of a mountain, g will decrease, therefore, T will increase. The pendulum will take more time to complete one vibration, i.e., it will lose time.
Q19. Given below are x - t plots for linear motion of a particle. Which of the plots represent periodic motion. What is the period of motion (in case of periodic motion)?


Solution
(i) It is not periodic as the motion is not repeated after a fixed point.
(ii) It is periodic with time period of 2 seconds as x - t graph is repeated after 2 seconds.
(iii) It is not periodic.
(iv) It is periodic with a period of 2 seconds as the x - t graph is repeated after 2 seconds.
Q20. An aeroplane passing over the building sometime causes rattling of windows of the building. Explain why?
Solution
If the frequency of the sound produced by the engine of aeroplane passing over building is equal to the natural frequency of windows of the building, then resonance takes place and causes the rattling of window.
Q21. The bottom of a dip on a road has a radius of curvature R. A rickshaw of mass M, left a little away from the bottom oscillates about this dip. Deduce the expression for the period of oscillation.
Solution
Let R be the radius of the dip and O be its centre. Let the rickshaw of mass M be at P at any instant. This case is similar to that of a simple pendulum. The force that produces oscillations in the rickshaw is F = Mgsin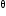 .
.

 .
.


Q22. Show that for a particle in linear simple harmonic motion, the average kinetic energy over a period of oscilllation is half the total energy.
Solution

Q23. What is the frequency of oscillation of a simple pendulum mounted in a cabin that is freely falling under gravity?
Solution
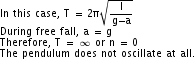
Comments
Post a Comment