Q1. A boat is moving with a velocity 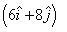 with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity
with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity 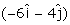 with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?
with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?
Solution
Q2. The position of a particle at any instant is given by 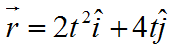 . What is the displacement of the particle in first three seconds?
. What is the displacement of the particle in first three seconds?
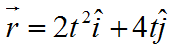 . What is the displacement of the particle in first three seconds?
. What is the displacement of the particle in first three seconds?Solution
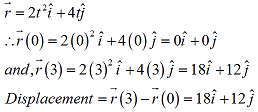
Q3. Given, 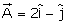 and
and 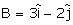 . The unit vector of
. The unit vector of 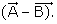 is
is
Solution
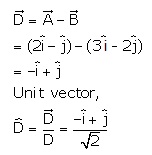
Q4. When a projectile is thrown up at an angle 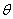 to the ground, the time taken by it to rise and to fall are related as
to the ground, the time taken by it to rise and to fall are related as
Solution
Time to rise is equal to time of fall.
Q5. If 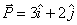 and,
and, 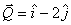 then, the product
then, the product 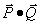 is
is
Solution
Q6. A monkey is running on the ground, next to a train, in the direction of the train. The speed of the monkey is 5km/h and the speed of the train is 100km/h. What is the velocity of the monkey with respect to the train?
Solution
Using
Vmonkey/train = Vmonkey/ground + Vground / train
Vground/train = - Vtrain/ground = -100 km/h
Vmonkey/ground = 5 km/h
Vmonkey/train = 5 -100 km /hr = -95 km/hr
Q7. The angular speed of the earth about its own axis is:
Solution
Q8. At maximum height during the journey of a projectile, which quantity becomes zero?
Solution
The vertical component of velocity becomes zero at maximum height.
Q9. The angular speed of the hour hand of a watch is :
Solution
Q10. Given, .gif) and
and .gif) Find the unit vector of
Find the unit vector of .gif)
Solution
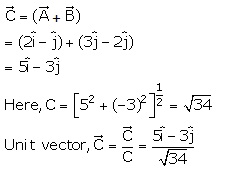
Q11. A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is
Solution
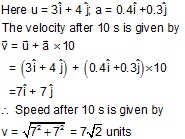
Q12. Two cars A and B are moving with same speed 30 km/hr in same direction with car B 5 km behind the car A. Another car C moving in opposite direction crosses the two cars at an interval of 4 minutes. Find the speed of car C.
Solution
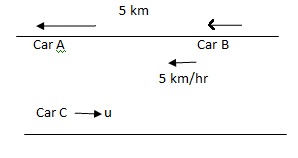 Let the car C is moving with velocity u km/hr. As the car B is 5 km behind the car A, therefore when the car C crosses the car A, it is 5 km from car B. Let us take left direction positive and right direction negative.
Therefore, velocity of car B = -5 km/hr
velocity of car C = + u km/hr
The relative velocity of car C w.r.t. car B
v = velocity of car C - velocity of car B
v = u - (-5) = (u+5) km/hr.
Now the car C travels 5 km distance with relative velocity (u+5) km/hr in 4 minutes.
Therefore, by using the relation, s = ut, we have
5 = (u+30) x (4/60)
or, 75 = (u+30)
or, u = 45 km/hr
Let the car C is moving with velocity u km/hr. As the car B is 5 km behind the car A, therefore when the car C crosses the car A, it is 5 km from car B. Let us take left direction positive and right direction negative.
Therefore, velocity of car B = -5 km/hr
velocity of car C = + u km/hr
The relative velocity of car C w.r.t. car B
v = velocity of car C - velocity of car B
v = u - (-5) = (u+5) km/hr.
Now the car C travels 5 km distance with relative velocity (u+5) km/hr in 4 minutes.
Therefore, by using the relation, s = ut, we have
5 = (u+30) x (4/60)
or, 75 = (u+30)
or, u = 45 km/hr
Q13. Two vectors are equal if and only if
Solution
Vectors are characterized by the magnitude as well as direction.
Q14. Having seen a big stone falling from the top of a tower Ravi pulled his friend Kiran away. The stone hit Ravi slightly and he got hurt. But he was saved from a major accident.
(a) What made Ravi act in such a way.
(b) From the top of a tower 100 m in height, a ball is dropped and at the same time another ball is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s. Find when and where the two balls meet. Take g = 9.8 m/sec2.
Solution
Q15. A boat is moving with a velocity .jpg) with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity
with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity 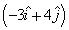 with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?
with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?
Solution

Q16. The angular speed of the second hand of a watch is :
Solution
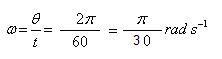
Q17. If the magnitude of two vectors is 4 and 5 and the value of their scalar product is 10, then the angle between vectors is:
Solution
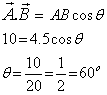
Q18. At the point of maximum height, the acceleration is:
Solution
At the point of maximum height, the acceleration is g.
Q19. A body of mass 15 kg revolves in a circle of diameter 1.20m, making 100 revolution per minute. Then, the linear velocity of body is:
Solution
.gif)
Q20. The only force which acts upon a projectile is
Solution
The only force which acts upon a projectile is Force of gravity.
Q21. At what angle should a projectile with initial velocity 'v' be thrown, so that it achieves its maximum range?
Solution
For maximum horizontal rangeHmax= (u2sin2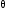 )/2g = (u2)/2g, implying the angle should be equal to 45°..
)/2g = (u2)/2g, implying the angle should be equal to 45°..
Q22. Find the area of the parallelogram formed by
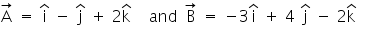
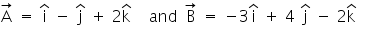
Solution

Q23. Rain is falling vertically with the speed of 60 m/s. A man rides a bicycle with the speed of 20 m/s in east to west direction. What is the direction in which he should hold the umbrella?
Solution
Speed of rain is: 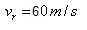 Speed of bicycle is :
Speed of bicycle is : .jpg) tan θ =
tan θ = 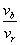 =
=
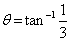
Q24. Find the component of vector 4 - 3
- 3 +
+  in the direction of 12
in the direction of 12 + 5
+ 5 -
- 
 - 3
- 3 +
+  in the direction of 12
in the direction of 12 + 5
+ 5 -
- 
Solution
we know  .
.  = AB cos
= AB cos Therefore, A cos
Therefore, A cos =
=  Now, component of
Now, component of  in the direction of
in the direction of  A cos
A cos
 =
= 
 =
= 
 Here,
Here,  = 4
= 4 - 3
- 3 +
+  and
and  = 12
= 12 + 5
+ 5 -
-  .
Thus,
.
Thus,  .
.  = 48 - 15 - 42 = -9
and
= 48 - 15 - 42 = -9
and  =
=  =
=  therefore, A cos
therefore, A cos
 =
= 
 =
= 

 .
.  = AB cos
= AB cos Therefore, A cos
Therefore, A cos =
=  Now, component of
Now, component of  in the direction of
in the direction of  A cos
A cos
 =
= 
 =
= 
 Here,
Here,  = 4
= 4 - 3
- 3 +
+  and
and  = 12
= 12 + 5
+ 5 -
-  .
Thus,
.
Thus,  .
.  = 48 - 15 - 42 = -9
and
= 48 - 15 - 42 = -9
and  =
=  =
=  therefore, A cos
therefore, A cos
 =
= 
 =
= 

Q25. A particle moves in x-y plane starting from the origin in a direction making 300 angle with x-axis. Distance covered by it is 5 m. what is the position vector of the particle.
Solution
x-component of position vector = 5 cos 30o = .gif) y-component of position vector = 5 sin 30o =
y-component of position vector = 5 sin 30o =.gif) position vector of particle =
position vector of particle = 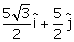
Q26. 

Solution
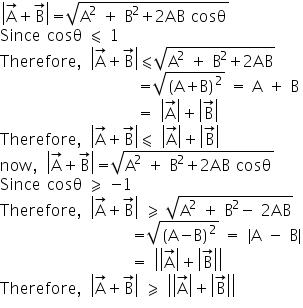
Q27. A cyclist starts from the center O of circle of park of radius 1 km, reaches the edge P of the park, then cycles along the circumference to point Q and returns to the centre along QO as shown. If the round trip takes 10 minutes, then what is
(a) net displacement
(b) average velocity
(c) average speed of the cyclist?


Solution
(a) Since the syclist starts from O and again returns to point O, therefore, displacement of cyclist is zero.
(b) Average velocity of the cyclist is zero because total displacement of the cyclist is zero.
(c) Total distance travelled by cyclist is
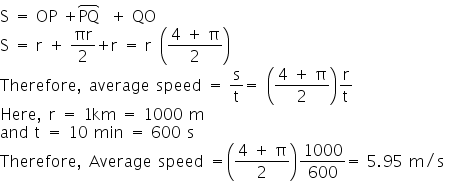
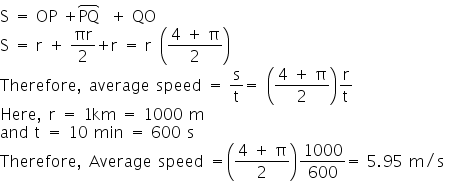
Q28. The distance travelled by an object along the axes are given by x = 2t2 ,y = t2-4t, z = 3t - 5 . The initial velocity of the particle is
Solution
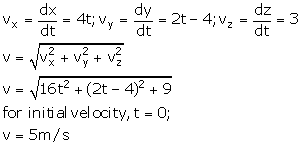
Q29. If 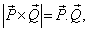 what is the angle between
what is the angle between 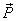 and
and 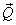
Solution
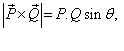
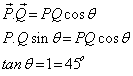
Q30. A car travelling at 36 km/h-1 due North turns West in 5 seconds and maintains the same speed. What is the acceleration of the car?
Solution
36 km/h = 10 m/s
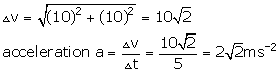
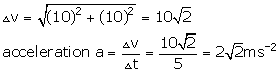
Q31. What is the angle between the vectors
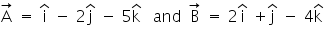
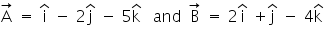
Solution

Q32. Two forces, whose magnitude are at the ratio of 3:5 give a resultant of 35 N. If angle of inclination is 60o, then the magnitude of each force is:
Solution
Let the two forces be: 3x and 5x
Resultant = 35 N
Angle of inclination: 60o
Now, according to parallelogram law of vector addition, we have:
R= 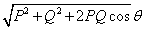 35 N =
35 N = 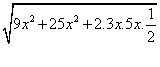 After solving above equation, we get:
x = 5 and two forces are: 15N and 25N respectively.
After solving above equation, we get:
x = 5 and two forces are: 15N and 25N respectively.
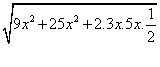 After solving above equation, we get:
x = 5 and two forces are: 15N and 25N respectively.
After solving above equation, we get:
x = 5 and two forces are: 15N and 25N respectively.
Q33. Angle between the vectors 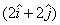 and
and 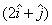 is:
is:
Solution
As
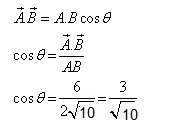
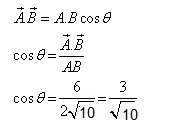
Q34. Find the value of n so that vectors,  are mutually perpendicular.
are mutually perpendicular.
 are mutually perpendicular.
are mutually perpendicular.Solution

Q35. The vector product of parallel vectors is always:
Solution
Q36. Two particles A and B start from P and move along a circular path in anticlockwise and clockwise direction respectively. They complete one fourth of the journey in the same time. Do they have same average velocities?
Solution
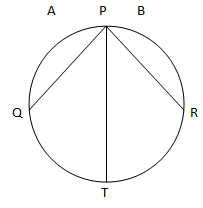 No, the two particles do not have same average velocities, because two particles undergo different displacements. But magnitude of displacement i.e. distance traveled by the two particles is same, therefore they have same speed.
No, the two particles do not have same average velocities, because two particles undergo different displacements. But magnitude of displacement i.e. distance traveled by the two particles is same, therefore they have same speed.
Q37. A force of 20 N acts on a body and displaces it 2m along the direction of force. Then the work done by the force is:
Solution
W = F.S cos θo = 20 × 2 cos 0o = 40 J
Q38. The quantity which remains unchanged during the flight of an oblique projectile is
Solution
The quantity which remains unchanged during the flight of an oblique projectile is horizontal component of velocity
Q39. An aircraft is flying at a height of 3400m above the ground. If the angle subtended at a ground observation point by the aircraft positions 10 s apart in 30o , what is the speed of the aircraft?
Solution
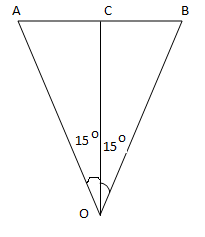 The aircraft takes 10s to go from A to B and AB subtends an angle 30o at O.
In right angled triangle OAC,
AC = OC tan 15o = 3400 x 0.2679 = 911 m
Therefore, AB = 2 x 911 = 1822 m
Now, the speed of aircraft
v = AB/t = 1822 / 10 = 182.2 m/s
The aircraft takes 10s to go from A to B and AB subtends an angle 30o at O.
In right angled triangle OAC,
AC = OC tan 15o = 3400 x 0.2679 = 911 m
Therefore, AB = 2 x 911 = 1822 m
Now, the speed of aircraft
v = AB/t = 1822 / 10 = 182.2 m/s
Q40. 

Solution
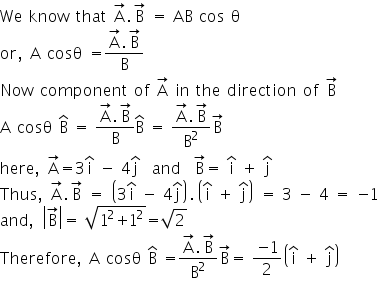
Q41. A jet airplane traveling at the speed of 500 km/hr ejects its products of combustion at the speed of 1500 km/hr relative to the jet plane. What is the speed of the later with respect to an obserever on the ground?
Solution
Let Vg be the velocity of ejecting gases with respect to ground.
velocity of jet plane Vj = + 500 km/hr
Velocity of ejected products w.r.t. jet plane
Vgj = Vg - Vj
or, Vg = Vgj + Vj
= -1500 + 500 = -1000 km/hr
Q42. A man can swim with speed of 4 km/hr in still water. How long does he take to cross the river 1 km wide if the river flows steadily at 3 km/hr and he makes his stroke normal to the river current? How far down the river does he go when he reaches the other bank?
Solution
Since the swimmer dive the river normal to the flow of river, therefore time taken by swimmer to cross the river 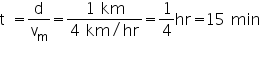
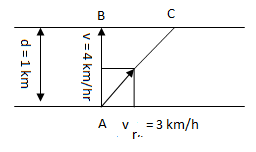 In this time the swimmer will also go down the river by distance BC due to river current.
In this time the swimmer will also go down the river by distance BC due to river current.
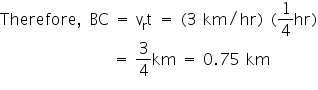
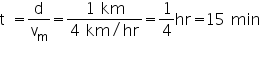
 In this time the swimmer will also go down the river by distance BC due to river current.
In this time the swimmer will also go down the river by distance BC due to river current.
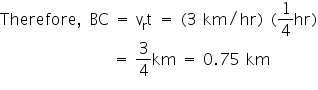
Q43. A motor boat, with its engine on in running river and blown over by a horizontal wind is observed to travel at 20 km/hour in a direction 53º east of north. The velocity of the boat with its engine on in still water and blown over by the horizontal wind is 4 km/hr eastward and the velocity of the boat with its engine on over the running river, in the absence of wind is a 8 km/hr, due south. Calculate
(a) the velocity of the boat in magnitude and direction over still water in the absence of wind,
(b) the velocity of the wind in magnitude and direction.
Solution
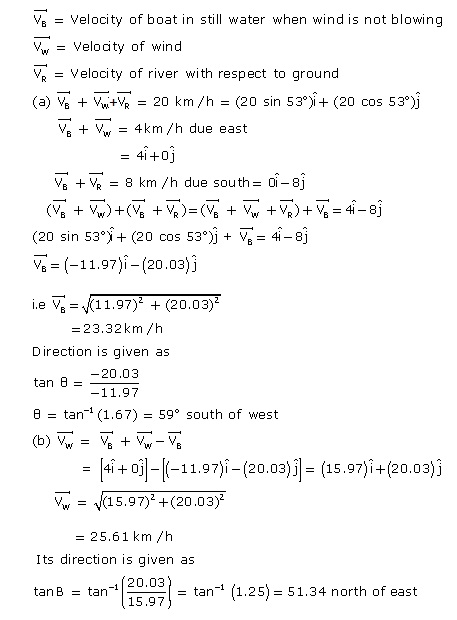
Q44. A projectile is fired at a falling target. The projectile leaves the gun at the same instant that the target falls from rest. Assuming that the gun is initially aimed at the target, show that the bullet will hit the target.
Solution
Let xB and yB be the x and y positions of the bullet, and let xT and yT be the x and y positions of the target. We need to show that, yB = yT and xB = xT at some common time tc , the time at which the bullet will hit the target.
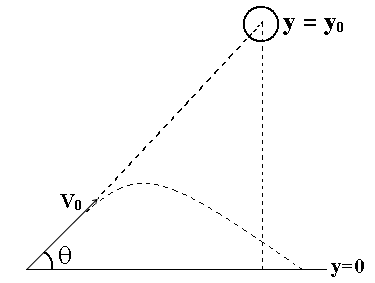 The motion of the bullet is described by the two equations: xB =v0cos θt yB =v0sin θt - (1/2) gt 2.
The bullet will take some time, tc, to arrive at the x position of the target, xT.
At that time, the bullet and target will be at the same x position (the target's x position does not change since it falls straight down). Thus, we have at time tc xT = xB = v0cos θ tc
At time tc, in order for the bullet to hit the target, the y positions must be equal at tc. The y position of the target is given by yT = y0 -(1/2) g tc2
and for the bullet
yB = v0sin θ tc - (1/2) gtc2.
We can see from the above equations that in order for yB = yT at tc , we need to have y0 = v0sinθ tc .
The motion of the bullet is described by the two equations: xB =v0cos θt yB =v0sin θt - (1/2) gt 2.
The bullet will take some time, tc, to arrive at the x position of the target, xT.
At that time, the bullet and target will be at the same x position (the target's x position does not change since it falls straight down). Thus, we have at time tc xT = xB = v0cos θ tc
At time tc, in order for the bullet to hit the target, the y positions must be equal at tc. The y position of the target is given by yT = y0 -(1/2) g tc2
and for the bullet
yB = v0sin θ tc - (1/2) gtc2.
We can see from the above equations that in order for yB = yT at tc , we need to have y0 = v0sinθ tc .
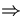 tan θ =
tan θ = 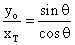
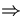 y0 = xT
y0 = xT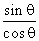 .
Using the previous result, xT = v0cos θ tc
or cos θ = (xT)/(v0tc)
which gives: y0 =
.
Using the previous result, xT = v0cos θ tc
or cos θ = (xT)/(v0tc)
which gives: y0 = 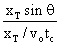 = v0sin θ tc.
Thus we have shown that at time tc , xT = xB and yT = yB, and therefore that the bullet will hit the target.
= v0sin θ tc.
Thus we have shown that at time tc , xT = xB and yT = yB, and therefore that the bullet will hit the target.
 The motion of the bullet is described by the two equations: xB =v0cos θt yB =v0sin θt - (1/2) gt 2.
The bullet will take some time, tc, to arrive at the x position of the target, xT.
At that time, the bullet and target will be at the same x position (the target's x position does not change since it falls straight down). Thus, we have at time tc xT = xB = v0cos θ tc
At time tc, in order for the bullet to hit the target, the y positions must be equal at tc. The y position of the target is given by yT = y0 -(1/2) g tc2
and for the bullet
yB = v0sin θ tc - (1/2) gtc2.
We can see from the above equations that in order for yB = yT at tc , we need to have y0 = v0sinθ tc .
The motion of the bullet is described by the two equations: xB =v0cos θt yB =v0sin θt - (1/2) gt 2.
The bullet will take some time, tc, to arrive at the x position of the target, xT.
At that time, the bullet and target will be at the same x position (the target's x position does not change since it falls straight down). Thus, we have at time tc xT = xB = v0cos θ tc
At time tc, in order for the bullet to hit the target, the y positions must be equal at tc. The y position of the target is given by yT = y0 -(1/2) g tc2
and for the bullet
yB = v0sin θ tc - (1/2) gtc2.
We can see from the above equations that in order for yB = yT at tc , we need to have y0 = v0sinθ tc .
Q45. The position of a particle at any instant is given by  .
At what instant the velocity vector will make an angle 45o with X-axis.
.
At what instant the velocity vector will make an angle 45o with X-axis.
 .
At what instant the velocity vector will make an angle 45o with X-axis.
.
At what instant the velocity vector will make an angle 45o with X-axis.Solution

Q46. A gun is kept on a straight road is used to hit a car traveling along the same road away from the gun with a uniform speed of 72 Km/h. When the gun is fired at an angle of 450, the distance between the car and gun was 500 m. find the speed of the projection of the shell from the gun? 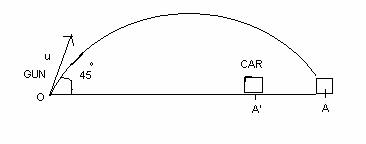

Solution
Let us suppose that at the instant, the shell is fired from the gun at the point O, the car is at the point A'.
Let the time of flight be=T
and horizontal range, OA =R
angle of projection. velocity of car =72 km/h =20m/s
It means that the shell will hit the car, if the car moves a distance A'A in the time T.
If v is the velocity of the car, then A'A=v T
Since the car is initially at the distance of 500m from the gun, therefore
R= OA' + A'A = 500 + v T (i)
Let u be velocity of projection of the shell. Then,
velocity of car =72 km/h =20m/s
It means that the shell will hit the car, if the car moves a distance A'A in the time T.
If v is the velocity of the car, then A'A=v T
Since the car is initially at the distance of 500m from the gun, therefore
R= OA' + A'A = 500 + v T (i)
Let u be velocity of projection of the shell. Then,
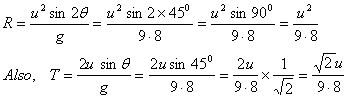 Substituting values of R,T and v in equation (i), we get
Substituting values of R,T and v in equation (i), we get
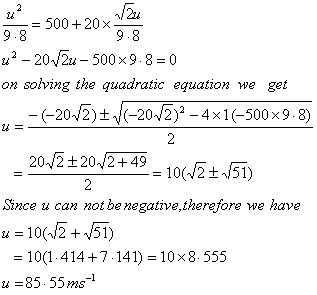
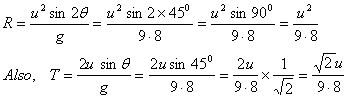 Substituting values of R,T and v in equation (i), we get
Substituting values of R,T and v in equation (i), we get
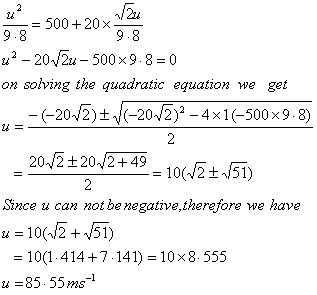
Q47. If a projectile is thrown with a velocity 10 ms-1 at an angle of 300 with the horizontal. Then the time of flight will be
Solution
Q48. The vector which when added to the resultant of 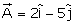 and
and 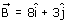 gives unit vector along x direction.
gives unit vector along x direction.
Solution

Q49. At what angle do the two vectors of magnitude A+B and A-B act so that their resultant is 

Solution

Q50. A projectile is thrown at an angle of 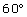 with the horizontal, with a speed of
with the horizontal, with a speed of 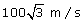 . Find (a) the time of flight (b) horizontal range.
. Find (a) the time of flight (b) horizontal range.
Solution
(a) The expression for the time of flight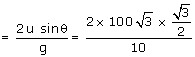 = 30 seconds
(b) Horizontal range
= 30 seconds
(b) Horizontal range 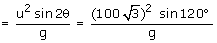
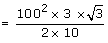
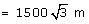
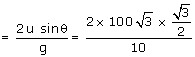 = 30 seconds
(b) Horizontal range
= 30 seconds
(b) Horizontal range
Q51. What is the ratio of maximum range and height for a projectile for an angle at which range is maximum ?
Solution
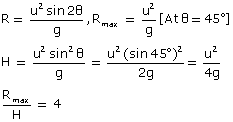
Q52. A plane drops a package of emergency rations to a stranded party of explorers. The plane is traveling horizontally at 40.0 m/s at 100 m above the ground. Find a) where the package strikes the ground relative to the spot it was dropped and b) the velocity of the package just before it hits the ground. 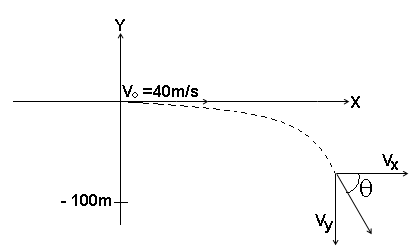

Solution
Consider the x and y components separately.
x-motion
y-motion
x =?
y = - 100 m
v0x = 40 m/s
v0y = 0
ax = 0
ay = - 9.8 m/s 2
a) We know that the time of flight is given by y=voyt + (1/2) ay t 2
- 100 = (1/2) (- 9.8) t 2
t = 4.5 s.
Then we can find x from, x =vx0t + (1/2) ax t 2
x = 40(4.5) + 0
= 180 m.
b) We find vy from,
vy = vy0 + at
= 0 - 9.8(4.5) = - 44.1 m/s.
Note that the negative sign correctly indicates that the package falls downward.
Since ax = 0 , we have vx = v0x = 40 m/s .
We can combine the two velocity components to obtain,
v = 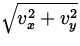 = 59.5 m/s
= 59.5 m/s
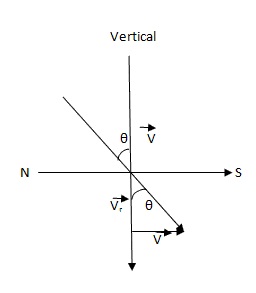
Q53. Rain is falling vertically with speed of 30 m/s. A woman rides a bicycle with a speed of 10 m/s in N to S direction. In which direction she should hold the umbrella?
Solution

Q54. Prove that the vectors  and
and  are perpendicular to each other.
are perpendicular to each other.
 and
and  are perpendicular to each other.
are perpendicular to each other.Solution
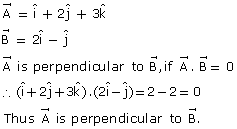
Q55. Two trains are moving in the opposite directions on parallel tracks, one with a velocity twice that of other. If the total length of the two trains is 480 ft and they take 3 seconds to cross each other, find their individual velocities.
Solution
Let the two trains A and B be moving in opposite directions with with velocities u ans 2u respectively.
Relative velocity V = u + 2u = 3u
Total distance moved = total length of the two trains S = 480 ft.
time taken by the trains to cross each other t = 3 seconds
Now, S = Vt
or, 480 = 3u x 3
or, u = 53.33 ft/s
and 2u = 106.66 ft/s
Q56. Two bodies are thrown with the same velocity, but at angles θ and 90 - θ with respect to the horizontal. Find the ratio of the maximum heights reached by the bodies.
Solution
Maximum height, 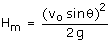 for the 1st projectile, the maximum height,
for the 1st projectile, the maximum height, 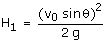 similarly,
similarly, 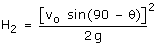
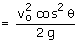
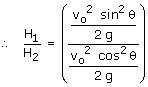
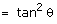
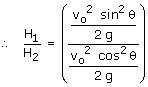
Q57. A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 with a velocity of  m/s and moves in XY plane with a constant acceleration of
m/s and moves in XY plane with a constant acceleration of  .
(a) At what time is the X-coordinate of the particle 16 m?
(b) What is the Y-coordinate of the particle at that time?
.
(a) At what time is the X-coordinate of the particle 16 m?
(b) What is the Y-coordinate of the particle at that time?
 m/s and moves in XY plane with a constant acceleration of
m/s and moves in XY plane with a constant acceleration of  .
(a) At what time is the X-coordinate of the particle 16 m?
(b) What is the Y-coordinate of the particle at that time?
.
(a) At what time is the X-coordinate of the particle 16 m?
(b) What is the Y-coordinate of the particle at that time?Solution
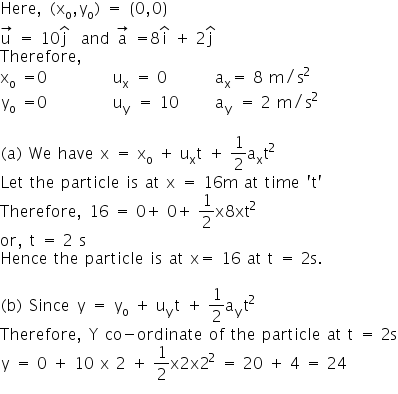
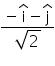
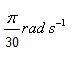
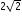 ms-2 South West
ms-2 South West
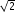 ms-2 South West
ms-2 South West
Comments
Post a Comment