Solution
Take the reference point home as the origin.1 hour: With respect to home the person moves to office: Motion is along +x axis.
2 hours: He stays at rest there
1/2 an hour: He moves back towards home: his x-coordinate with respect to the origin decreases.
Q2. The displacement of a particle along x-axis is given by x = 4 + 6t + 5t2. Its acceleration at t = 2s
Solution

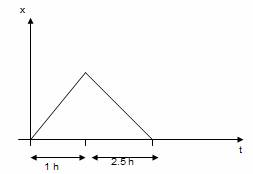
Q3. What type of motion dos the following graph represent? .jpg)
.jpg)
Solution
The graph represents a case where the velocity of the object goes on increasing with time.
Q4. A train 100 m long is running with speed of 40 km/h. In what time shall it cross a bridge of 1 km length?
Solution
Distance = 100 + 1000 = 1100 m
Speed = 40 km/h = 11.11 m/s
Time = Distance/Speed = 1100/11.11 = 99 s
Q5. If we choose the upward direction as positive which of the following graphs correctly represents the acceleration of a freely falling body? 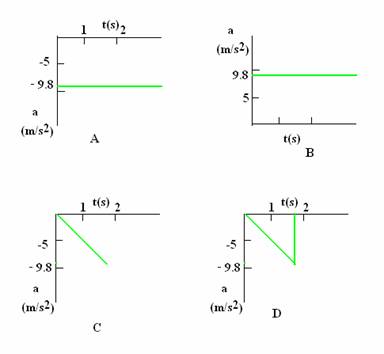

Solution
A since upward direction is given as positive the downward direction will be negative. All throughout the acceleration remains -9.8m/s2.
Q6. 36 km/h is equal to:
Solution
36 km/h = 36 x 103 m/3600 s = 10 m/s
Q7. Suppose our school is 1 km away from our house, and we go to school in the morning, and in the afternoon we come back. Then, the total displacement for the entire trip is
Solution
Displacement is zero in this case.
Q8. The position of a particle is given by x = at3 where a is a constant. Find the velocity as a function of time.
Solution
Velocity = dx/dt = a.3t2 = 3at2
Q9. On velocity-time graph when two curves coincide, the objects will have
Solution
On velocity-time graph, the point at which two curves coincide will indicate that both the objects have same velocity at that instant.
Q10. The graph represents the velocity time for the first 4 seconds of motion. The distance covered is .jpg)
.jpg)
Solution
The distance covered = area under the curve = (1/2) x 4 x 15 = 30 m
Q11. What is the distance of the star (in km) from which a light takes 3 x 109 year to reach the earth? The speed of light, is C = 3 x 108 m/s.
Solution
Time = 3 x 109 x 365 x 24 x 60 x 60 = 9.46 x 1016 s
Distance = speed x time = 3 x 108 m/sx 9.46 x 1016 s = 2.838 x 1022 km
Q12. Rain falls at a speed of 50m/s and a child walks on a straight road from east to west at a speed of 100m/s. To find the direction in which the child should hold the umbrella use
Solution
Rain falls at a speed of 50m/s and a child walks on a straight road from east to west at a speed of 100m/s. To find the direction in which the child should hold the umbrella use relative speed of rain with respect to child.
Q13. An aeroplane lands on a runway with a velocity of 50 m/s. It decelerates at 10 m/s2 to a velocity of 20 m/s. Find the time elapsed.
Solution
Use v = u + at
20 = 50 - 10 t
t = 3s
Q14. If a body does not change its direction during the course of its motion, then
Solution
Path length and displacement becomes equal if an object does not change its direction.
Q15. A stone and a feather are dropped from the same height H=1 m in an evacuated chamber. Which object will reach the bottom of the chamber first?
Solution
The acceleration is the same for all objects on earth, and is equal in magnitude to g=9.8 m/s2. Since both objects obey the same kinematics equations (and are both dropped from rest at the same time), they must follow identical trajectories.
Q16. The displacement-time graph shows the following: .jpg)
.jpg)
Solution
An object starting from s = 10 m and having constant positive velocity.
Q17. The ratio of magnitude of velocity and speed is always:
Solution
The displacement of the body in given time is always equal to or less than distance covered, because, velocity is displacement per unit time and speed is distance covered per unit time, therefore, ratio of magnitude of velocity and speed is always equal to or less than one.
Q18. A car moving with a speed of 50 km/h can be stopped by applying brakes after at least 10 m. What will the minimum stopping distance if the same car is moving at a speed of 100 km/h?
Solution
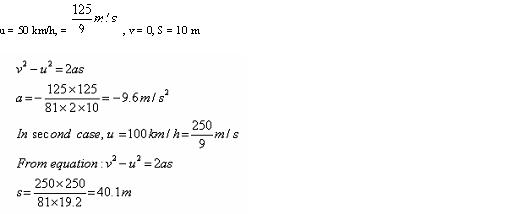
Q19. The position x of a particle varies with time (t) as
x = at2 - bt3
The acceleration of the particle will be zero at time
Solution
x = at2 - bt3
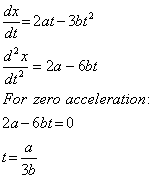
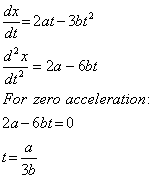
Q20. In the following x-t graph, which path represents the displacement .jpg)
.jpg)
Solution
Shortest path is displacement.
Q21. On acceleration-time graph, a horizontal line indicates:
Solution
A horizontal line on a acceleration- time graph indicates that object has constant acceleration.
Q22. In the graphic seen, find the (a) Speed of trolley with respect to person (2) (b) Speed of person (1) with respect to person (2). 

Solution
(a) We want to find Vt2= velocity of trolley with respect to person 2. the velocity of the trolley with respect to the ground, Vtg=20m/s
And the velocity of person 2 with respect to ground V2g=-2m/s. Also, since Vab= - Vba, we know that Vg2= +2m/s.
Using our formula, we have:
Vt2 = Vtg+ Vg2 = 20 m/s + 2m/s = 22 m/s.
(b)
We want to find V12=V1g+Vg2. Vg2 = 2m/s we know V1t = -5m/s, and
Vtg = +20 m/s. Therefore V1t + Vtg=15m/s=V1g
So, V12= 15 m/s + 2 m/s = 17 m/s towards right.
Q23. The speed of an object in a particular direction is called
Solution
The speed of an object in a particular direction is called velocity.
Q24. The distances traversed by a freely falling body, falling from rest, in equal intervals of time is in the following ratio ____________.
Solution
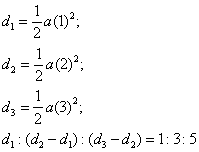
Q25. An orange is dropped from a building. One second after dropping the orange, it falls one storey. Two seconds after the orange is dropped, how many stories has it fallen?
Solution
That is because the kinematics equation says that y= (1/2) g t2


Q26. A man starts from his home with a speed of 4 km/h on a straight road up to his office 5 km away and returns to home, then the path length covered is
Solution
The path length depends on the actual path covered by the object. Here path length is (5 + 5) km = 10 km
Q27. A boy throws up a ball in a stationary lift and the ball returns to his hands in 10 s. Now if the lift starts moving up at a speed of 5 m/s. The time taken for a ball thrown straight up to return to his hands is:
Solution
The uniform velocity of the lift does not affect the relative velocity of the ball with respect to the boy. So, the ball will still return in 10 s.
Q28. A bullet fired into a fixed target loses half of its velocity after penetrating 3 cm. How much further will it penetrate before coming to rest?
Solution
If u is the initial velocity, then v = u/2, S = 3 cm
.jpg)
.jpg)
Q29. Speed time graph of a particle moving along a fixed direction is shown in the figure below. The average speed of the particle over the interval: t = 0 s to 10 s. 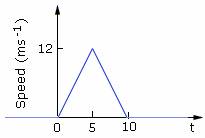

Solution
Distance traveled from t = 0 s to t = 10 s= area under curve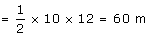
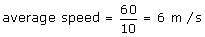
Q30. The displacement of a particle is represented by the following equation .gif) where s is in metres t in seconds. The acceleration of the particle at t = 1 s is
where s is in metres t in seconds. The acceleration of the particle at t = 1 s is
Solution
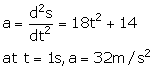
Q31. Two stones of different masses are thrown vertically upward with same initial velocity. Which one will rise to a greater height?
Solution
Both the stones will rise to the same height. It is because, for a body moving with given initial velocity and acceleration, the distance covered is same. It does not depend on body's mass.
Q32. A ball is thrown vertically upward. At the highest point in its path, which of the following statements is correct?
Solution
The acceleration due to gravity is constant throughout the flight of the ball. It's magnitude is g=9.8 m/s2, and it is the same at all points that the ball is not in contact with the ground or your hand. It is the velocity that is zero.
Q33. Velocity vs time graph of a particle moving along a straight line is shown.  What is the average acceleration between t = 4 s and t = 12 s?
What is the average acceleration between t = 4 s and t = 12 s?
 What is the average acceleration between t = 4 s and t = 12 s?
What is the average acceleration between t = 4 s and t = 12 s?Solution
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
At t = 4 s and 12 s, v = 10 m/s and -10 m/s respectively.Final velocity = -10 m/s, and the initial velocity = 10 m/s. Thus acceleration = (vf-v0)/t = (-10 - 10)/ (12-4) = -2.5 m/s2
Q34. If a particle is moving in a spiral path with constant speed, then:
Solution
As the particle is moving in spiral path with constant speed, its magnitude remains constant whereas direction changes continuously. Thus, the magnitude of acceleration also remains constant.
Q35. An object which is moving with a speed of u m/s applied brakes and achieves a retardation of magnitude 'a' m/s2. Find the distance it would cover before stopping.
Solution
Initial velocity = u and acceleration = -a final velocity = 0 Therefore, applying 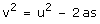
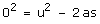
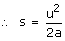 Therefore, the stopping distance
Therefore, the stopping distance 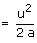
Q36. A worker drops a hammer from the top of a 60m high building. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s, how long does the worker have to shout down to warn colleagues (if his warning is to reach them before the hammer!) Neglect air resistance.
Solution
For the hammer:
Initial speed u = 0
Acceleration a = 9.81 m/s2
Distance s = 60m
Using the second equation of motion, we get
 The length of time for the hammer to reach the ground minus the length of time it takes for the shouted warning to reach the workers on the ground gives the difference in travel time between hammer and shout.
That is, 3.5 - 0.18 = 3.32 s
Therefore the warning must be shouted within 3.32 seconds of dropping the hammer.
The length of time for the hammer to reach the ground minus the length of time it takes for the shouted warning to reach the workers on the ground gives the difference in travel time between hammer and shout.
That is, 3.5 - 0.18 = 3.32 s
Therefore the warning must be shouted within 3.32 seconds of dropping the hammer.
 The length of time for the hammer to reach the ground minus the length of time it takes for the shouted warning to reach the workers on the ground gives the difference in travel time between hammer and shout.
That is, 3.5 - 0.18 = 3.32 s
Therefore the warning must be shouted within 3.32 seconds of dropping the hammer.
The length of time for the hammer to reach the ground minus the length of time it takes for the shouted warning to reach the workers on the ground gives the difference in travel time between hammer and shout.
That is, 3.5 - 0.18 = 3.32 s
Therefore the warning must be shouted within 3.32 seconds of dropping the hammer.
Q37. Which of the following quantity remains constant during the uniform circular motion?
Solution
When a body is in uniform circular motion, its speed remains constant but its velocity, angular acceleration, angular velocity changes due to change in its direction.
Q38. The dimensions of instantaneous acceleration is:
Solution
The dimension is same as acceleration.
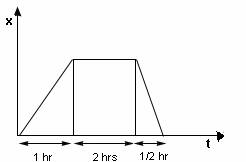
Q39. What type of motion do the following graphs represent? 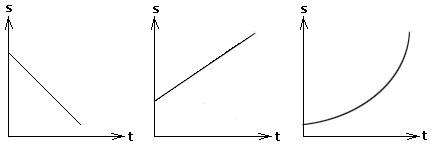

Solution
a) The first graph represents negative velocity, that is, an object moving along the negative side of the axis.
b) The second graph similarly represents constant positive velocity that is, an object moving along the positive side of the axis.
c) The third graph represents a case where the velocity of the object goes on increasing with time.
Q40. The graph represents the velocity time for the first 4 seconds of motion. Find the distance covered. 

Solution
The distance covered = area under the curve 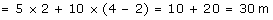
Q41. Two escalators move people up and down between floors of a shopping mall at the same rate, either up or down. What of the following statements regarding the motion of the escalators is true?
Solution
Velocity can vary when speed is constant.
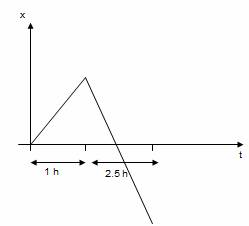
Q42. What does this graph indicate about the motion of an object?


Solution
This graph indicate that object is moving in positive direction with negative acceleration.
Q43. Slope of displacement time graph or x-t graph gives us the particles' ____________.
Solution
The slope of displacement time graph gives the velocity. It can be verified dimensionally since the slope will have dimension of displacement over times which has dimension of velocity.
Q44. What does this graph indicate about the motion of an object?.jpg)
.jpg)
Solution
This graph indicates that object is moving in positive direction with negative acceleration.
Q45. A train is moving with speed of 100 km/h. What is the speed of train in the reference frame of an observer standing on the road and an observer moving with the speed of 5 km/h in a direction opposite to the train?
Solution
For an observer standing on the road, the speed of the train is 100 km/h.
For an observer moving on the road with the speed of 5 km/h, the speed of train is 100 + 5 = 105 km/h.
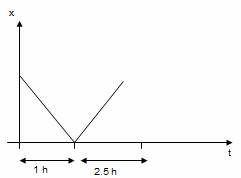
Q46. What does this graph indicate about the motion of an object?


Solution
An object is moving in positive direction till time t1, and then turns back with the same negative acceleration.
Q47. A bullet fired into a fixed target loses half of its velocity after penetrating 3 cm. What will be its acceleration?
Solution
If u is the initial velocity, then v = u/2, S = 3 cm
.jpg)
.jpg)
Q48. A car moves along x axis with constant acceleration= 2m/s2. At time t=0, the car is at position x= 4 m and has velocity =2m/s. a. Find the position and velocity at time t=2s. b. Where is the body when the velocity becomes 5m/s?
Solution
Following is the data identified as given in the problem:
xo= 4m; vo =2m/s; a = 2m/s2
a) From the equation of motion: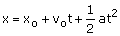
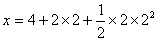 x =12 m The car will be located at position x=12 m with respect to the initial point from where it started. Next to determine the velocity of the car at instant t=2s using
x =12 m The car will be located at position x=12 m with respect to the initial point from where it started. Next to determine the velocity of the car at instant t=2s using 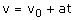
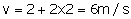 The car will cross the position x=12 m at instant t=2s with velocity 6 m/s.
b) Now let us locate the position of the car when its velocity would becomes 5m/s. Using
The car will cross the position x=12 m at instant t=2s with velocity 6 m/s.
b) Now let us locate the position of the car when its velocity would becomes 5m/s. Using 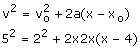
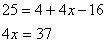 or x= 9.25 m Therefore the car will be at position 9.25 m with respect to the initial point, when its velocity becomes 5m/s.
or x= 9.25 m Therefore the car will be at position 9.25 m with respect to the initial point, when its velocity becomes 5m/s.
Q49. The position x of a particle varies with time (t) as x = 3t2 – 2t3 The acceleration of the particle will be zero at time
Solution
Use d2x / dt2 = 0
d/dt (3t2 – 2t3) = 6t - 6t2 =0
d/dt (6t - 6t2 ) = 6 - 12 t =0
i e 12 t =6
t= 1/2
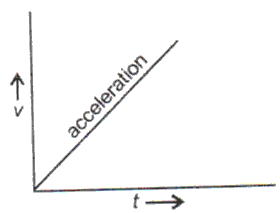
Q50. Draw velocity - time graph for an object with constant and positive acceleration.
Solution
The velocity - time graph for an object with constant and positive acceleration:.

Q51. The displacement of a particle starting from rest (at t = 0) is given by s = 6t2-t3 The time in seconds at which the particle will attain zero velocity again, is
Solution
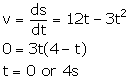 Here t = 0 is not realistic so at t = 4s the velocity will be zero.
Here t = 0 is not realistic so at t = 4s the velocity will be zero.
Q52. A stone is dropped from a height of 2000 m. After striking the ground it rebounds with a velocity half that of the velocity before striking. Find the maximum height reached after this rebound. Take .
.
Solution
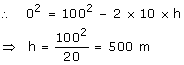
Q53. The position of the particle along x-axis varies with time as
x = 4t2 - 6t + 1, then:
(a) What is the velocity at t = 0?
(b) When does velocity become zero?
Solution
For rectilinear motion, velocity of an object can be calculated as:
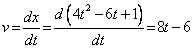 a) The velocity at t = 0,
v = 8t - 6 = - 6 m/s
b) For v = 0
v = 8t - 6
0 = 8t - 6
8t = 6
t= 6/8
At t= 3/4 sec, the velocity becomes zero
a) The velocity at t = 0,
v = 8t - 6 = - 6 m/s
b) For v = 0
v = 8t - 6
0 = 8t - 6
8t = 6
t= 6/8
At t= 3/4 sec, the velocity becomes zero
Q54. A particle moves along a straight line such that its displacement at any time t is given by 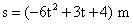 . Show that the acceleration is constant, and find the velocity of the particle at t=3 s.
. Show that the acceleration is constant, and find the velocity of the particle at t=3 s.
Solution
The displacement at time t,
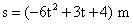 Instantaneous velocity,
Instantaneous velocity,
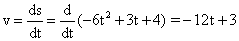 ms-1
And instantaneous acceleration,
ms-1
And instantaneous acceleration,
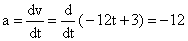 ms-2
So the acceleration is constant.
Then, from the velocity equation,
ms-2
So the acceleration is constant.
Then, from the velocity equation, 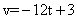 =-33m/s
Here, negative velocity means that the body is moving towards the origin, that is,
as time advances, displacement decreases.
=-33m/s
Here, negative velocity means that the body is moving towards the origin, that is,
as time advances, displacement decreases.
Q55. The velocity- time graph for a vehicle is shown. Draw the acceleration time graph from it. 

Solution
In time 1 to 3 s, acceleration of the vehicle is:
 a = slope of OA = 5 m/s2
In time 3 to 5 sec velocity of the particle remains same, hence acceleration = zero.
In time 3 to 5, acceleration of the vehicle is:
a = slope of BC = 5 m/s2
a = slope of OA = 5 m/s2
In time 3 to 5 sec velocity of the particle remains same, hence acceleration = zero.
In time 3 to 5, acceleration of the vehicle is:
a = slope of BC = 5 m/s2
 a = slope of OA = 5 m/s2
In time 3 to 5 sec velocity of the particle remains same, hence acceleration = zero.
In time 3 to 5, acceleration of the vehicle is:
a = slope of BC = 5 m/s2
a = slope of OA = 5 m/s2
In time 3 to 5 sec velocity of the particle remains same, hence acceleration = zero.
In time 3 to 5, acceleration of the vehicle is:
a = slope of BC = 5 m/s2
Q56.  An object starts from a point and moves on a smooth portion of land, where there is no friction. It then moves into an area with friction such that the retardation is
An object starts from a point and moves on a smooth portion of land, where there is no friction. It then moves into an area with friction such that the retardation is  . Find the total time and distance covered, before it stops.
. Find the total time and distance covered, before it stops.
 An object starts from a point and moves on a smooth portion of land, where there is no friction. It then moves into an area with friction such that the retardation is
An object starts from a point and moves on a smooth portion of land, where there is no friction. It then moves into an area with friction such that the retardation is Solution
To cover the first 100 m, it would take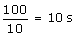 . The time taken before it finally stops in the rough patch is given by v = u + at0 = 10 + -2 t
. The time taken before it finally stops in the rough patch is given by v = u + at0 = 10 + -2 t 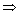 t = 5 sdistance covered in this part
t = 5 sdistance covered in this part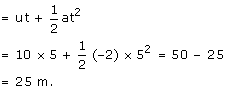
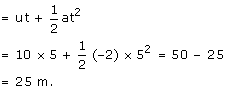
Q57. A ball is thrown is vertically upward. What is its velocity and acceleration at the top?
Solution
At highest point velocity of the particle is zero and its acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to gravity acting in the downward direction.
Q58. There is a bug who moves from point A to point B and then finally to C in 5 seconds. Are the speed and velocity of the bug Different? 

Solution
Physically, speed and velocity are different in the sense that the former is scalar, whereas the latter is a vector.
However, in terms of magnitude, in this case, both are equal. Magnitude of velocity = speed =
Magnitude of velocity = speed = 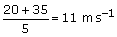 This is because the bug happens to move along a straight line and does not turn back, in other words, does not change direction during its travel from A to C.
This is because the bug happens to move along a straight line and does not turn back, in other words, does not change direction during its travel from A to C.
Q59. The velocity of the particle is given by v = 4t2 + 7 cm/s. Find the velocity of the particle during the time interval t1 = 2s and t2 = 4s also find the average acceleration during the same interval of time.
Solution
v = 4t2 + 7
When t1 = 2s, v1 = 4(2)2 + 7 = 23 cm/s
When t2 = 4s, v2 = 4(4)2 + 7 = 71 cm/s
Change in velocity = v2 – v1 = 71 – 23 = 48 cm/s
Average acceleration = 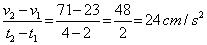
Comments
Post a Comment