Q1. The error in two readings of A are 0.01 and -0.03, then mean absolute error is ?
Solution
The absolute value of the errors is taken.
So mean absolute error = (0.01 + 0.03) / 2 = 0.02
Q2. The mass of a box measured by a grocer's balance is 2.3 kg. Two gold pieces of masses 20.15 g and 20.17 g are added to the box. What is the total mass of the box and account for its accuracy.
Solution
The total mass of the box is equal to the sum of the masses of box and constituents in the box.
i.e. M = 2.3 + 0.02015 + 0.02017 = 2.34032 kg
Since mass of the box is the least accurate because known to one tenth of kg only, therefore, the result must not be more accurate than one tenth of kg.
M = 2.3 kg
Q3. Find the option with 3 significant figures.
Solution
0.0268 have three significant figures where as 2.608 cm, 26.08 mm and 2.068 cm have four significant figures.
Q4. Three physical quantity having dimensions [M L-1 T-2] are
Solution
Pressure = Force/Area = ML1T-2/ L2 = [M L-1 T-2]
Stress = Force/Area = ML1T-2/ L2 = [M L-1 T-2]
Coefficient of elasticity = Stress/strain = [M L-1 T-2]
Q5. 1 unified atomic mass unit is equal to.
Solution
1 unified atomic mass unit is equal to 1/12 of the mass of carbon-12 [12C6] isotope.
Q6. A 5.2 g of a substance occupies 1.11 cm3. Its density to appropriate significant figure is:
Solution
There are 2 significant figures in measured mass whereas there are only 3 significant figures in measured volume. Hence density should be expressed to only 2 significant figures.
Q7. Magnitude of force F experienced by a certain object moving with speed v is given by F = Kv3, where K is a constant. The dimensions of K are
Solution
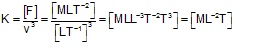
Q8. 1 fermi is equal to:
Solution
1fm = 10-15m.
Q9. The velocity 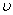 (in cm s-1) of a particle is given in terms of time t (in s) by the equation
(in cm s-1) of a particle is given in terms of time t (in s) by the equation 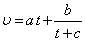 The dimensions of a, b and c are
The dimensions of a, b and c are
Solution
.gif)
.gif)
Q10. The nearest star to our solar system is 4.29 light year away. How much is this distance in terms of parsecs?
Solution

Q11. The number of significant figures in the distance of one light year , 9.4605 × 1015 m is
Solution
As the power of 10 is irrelevant in the determination of significant figures hence, the numbers of significant figures are 5.
Q12. The length of the rod as measured in an experiment was found to be 3.23 m, 3.25 m, 3.27 m, 3.22. Find the absolute error.
Solution

Q13. derive the expression for viscous force acting on spherical body of radius r moving with velocity v through viscous liquid of co-efficient of viscosity η.
Solution

Q14. Approximate ratio of 1 fermi to 1 angstrom is ..............
Solution
1 fermi = 10-15 m, 1angstrom = 10-10 m
Hence,1 fermi / 1angstrom = 10-15/ 10-10 = 10-5 m
Q15. The order of magnitude of a number expressed in scientific notation is
Solution
The order of magnitude of a number expressed in scientific notation is power of ten.
Q16. Which of the quantity is dimensionless?
Solution
Angle = length of Arc/ radius = L/L = 1 = [M0 L0 T0]
Q17. The most suitable instrument for measuring the size of an atom is.
Solution
Only electron microscope has resolution of 0.5-0.6 Angstrom which is less than the size of an atom.
Q18. Check the dimensional consistency in the following cases:
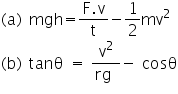
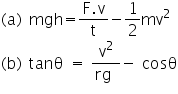
Solution

Q19. Angstrom is the unit of
Solution
Ao is the unit of length.
Q20. What is the dimension of (½)at2?
Solution
½ a t2 has the dimension of length since the dimension of acceleration is L/T2 and multiplying it by T2 leaves us with the dimension of length.
Q21. Relative error in Z, given that Z = 1/A2 is:
Solution
It is two times the error in A. If two quantities are multiplied or divided the relative error in the result is the sum of the relative errors in the multipliers.
Q22. Random errors occur due to:
Solution
They arise due to random and unpredictable fluctuations in experimental conditions (temperature, supply etc) and personal errors by the observer taking readings.
Q23. Express one parsec in terms of light year.
Solution
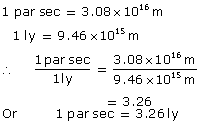
Q24. One angstrom is equal to __________ .
Solution
One angstrom (1o) is equivalent to 10-10m.
Q25. Find the percentage error, if the absolute error is 0.01 and average length of object is 3.25 m.
Solution
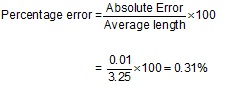
Q26. Given y = a sin (ωt - k x), where x is position and t is time. Show that ω / k has dimensions of velocity.
Solution

Q27. Find the dimensions of a and b in the Vanderwaal's equation

Solution

Comments
Post a Comment